* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells: The Basic Unit of Life - Warren County Public Schools
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
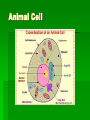
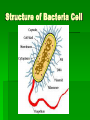
Cells: The Basic Unit of Life Organization of Life Everything has a least one cell Many living things exist as only one cell Other living things may have trillions of cells What is the world’s largest cell? The egg! The first cell of a chicken is the yolk with a tiny white dot in it. It is surrounded by a clear jellylike fluid called egg white. The white dot divides over and over again to become a chick. We are made up of about 100 trillion cells. We have about 200 different kind of cells and each is specialized to do a particular job Examples: blood cells, bone cells, nerve cells, skin cells Tissue A group of cells working in a team to perform a specific job. The material around and between the cells is also part of the tissue. Examples: blood, fat, muscle Organs When two or more tissues work together to perform a specific job, the group of tissue is called an organ. Examples: stomach, intestines, heart, lungs, skin Plants have different kinds of tissues that work together. The leaf is a plant organ, so is the stem and roots. Organ Systems Organs working together to perform particular jobs. Examples: digestive system, respiratory system, Organisms: Independent Living Anything that can live on its own is an organism. A single cell living on its own is called unicellular. An organism that exist only as a group of cells is called multicellular. Populations A group of organisms of the same kind living in the same area. Examples: deer population in a forest, people in a specific town or city, oak trees in a forest Communities Two or more populations living in the same area Example: foxes, oak trees, lizards, flowers, and many more make up the forest community. People, dogs, cats, and many more organism make your hometown community Ecosystem It is the community and all of the nonliving things that effect it, such as water, soil, temperature, and light. Complete the following sentence. Cells are related to _____________ in the same way that _____________ are related to organ system. Cell Theory In 1839 Theodor Schwann wrote the first two parts of the cell theory: All organisms are composed on one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. In 1858 Rudolf Virchow wrote the third theory: All cells come from existing cells. What do all cells have? Cell membrane- controls the passage of materials in and out of the cell DNA-controls all the activities of the cell and contains the information need for new cells. Cytoplasm-the fluid and almost everything in it Organelles-structures within the cell Two Types of Cells Prokaryotic No nucleus No membrane covered organelles Circular DNA Bacteria Eukaryotic Nucleus Membrane covered organelles Linear DNA All other cells Animal Cell Organelles in Animal Cell Cell membrane Lysosomes Nucleus Nucleolus Nuclear membrane vacuoles mitochondria Golgi body Cytoplasm Ribosomes Smooth ER Rough ER centrosomes Plant Cell Organelles In Plant Cell Organelles in yellow are only found in plant cells Cell wall Cell membrane Vacuoles (large) Nucleus Nucleolus Nuclear membrane Chloroplasts mitochondria Cytoplasm Amyloplast Centrosome Rough ER Smooth ER Ribosomes Golgi body Bacteria Cells Structure of Bacteria Cell Nucleolus The nucleolus primary function is to assemble ribosomes, is the largest structure in the cell nucleus.