* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
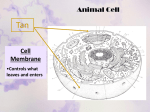
The Cell Chapter 2 - Cellular activity © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. K J I H A B C D E G F © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. K J I H Nucleus A B C D E G F The nucleus contains most of the cell’s DNA. DNA molecules in a cell contain a code that is the inherited information, or genes. The role of the genes is to determine the proteins that a cell can make. © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. K J I H A Nucleolus B C D E G F The nucleolus is mainly made up of RNA. RNA is involved in protein synthesis. mRNA reads DNA and carries the message to the ribosomes where the proteins are synthesised. tRNA brings the amino acids to the ribosomes to be joined into protein chains. © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. K J I H A B Endoplasmic C reticulum D E G F The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of membranous channels that store and transport materials. They also provide a surface on which chemical reactions occur. © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. K J I H A B C Cytoplasm D E G F The cytoplasm is the jelly-like fluid in which the organelles of the cell are suspended. This is also where many chemical reactions occur. © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. K J I H A B C D Golgi E apparatus G F The golgi body or golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins for secretion from the cell. © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. K J I H G Ribosomes F A B C D E Review protein synthesis The ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. They can be free in the cytoplasm or attached to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), making it rough ER. © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the Return to the cell. parts of the cell. K J I H A B C D E G F Review protein synthesis from Human Biology 2A-2B. © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. K J I H A B C D E CellG membrane F The cell membrane separates the cell contents from the environment. The membrane is semi-permeable and regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. K J A B C D I E Mitochondria H G F The mitochondria are the site of aerobic respiration. glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. K J Cytoskeleton I H A B C D E G F The cytoskeleton consists of micro-filaments and tubules, which support the cell. © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. K NuclearJ pore I H A B C D E G F The nuclear membrane contains pores, which allow large molecules to pass out of the nucleus. mRNA passes out of the nuclear pores during protein synthesis. © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia Click on the letters (in any order) to learn about the parts of the cell. Nuclear K membrane J I H A B C D E G F The nuclear membrane separates the nucleus from the cell. © 2010 McGraw-Hill Australia