* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure & Function - Mrs. Pace's Science Site
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
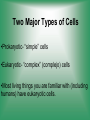
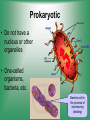
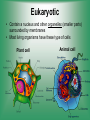
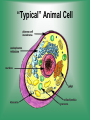
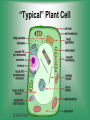
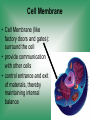
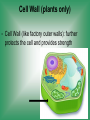
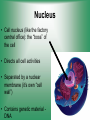
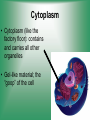
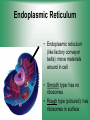
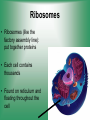
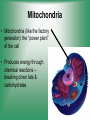
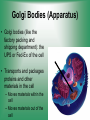
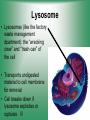
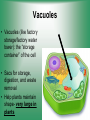
Cell Structure & Function 5/22/2017 4 Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Cell Theory (Teoría) 1. All living things are made up of cells. 2. Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. 3. All complex cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. Two Major Types of Cells •Prokaryotic- “simple” cells •Eukaryotic- “complex” (complejo) cells •Most living things you are familiar with (including humans) have eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic • Do not have a nucleus or other organelles • One-celled organisms, bacteria, etc. Bacteria cell in the process of reproducing (dividing) Eukaryotic • Contain a nucleus and other organelles (smaller parts) surrounded by membranes • Most living organisms have these type of cells Plant cell Animal cell Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Prokaryote: Both: Eukaryote: -are living -has no organelles (no nucleus) -have DNA -are cells -has organelles (has a nucleus) “Typical” Animal Cell “Typical” Plant Cell Cell Parts Organelles: “little organs” Think of a cell as a factory- lots of separate people, departments, and machines that each have their own task, but they work together to get a job done. Surrounding the Cell Cell Membrane • Cell Membrane (like factory doors and gates): surround the cell • provide communication with other cells • control entrance and exit of materials, thereby maintaining internal balance Cell Wall (plants only) • Cell Wall (like factory outer walls): further protects the cell and provides strength Inside the Cell Nucleus • Cell nucleus (like the factory central office): the “boss” of the cell • Directs all cell activities • Separated by a nuclear membrane (it’s own “cell wall”) • Contains genetic material DNA Cytoplasm • Cytoplasm (like the factory floor): contains and carries all other organelles • Gel-like material; the “goop” of the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum • Endoplasmic reticulum (like factory conveyor belts): move materials around in cell • Smooth type: has no ribosomes • Rough type (pictured): has ribosomes in surface Ribosomes • Ribosomes (like the factory assembly line): put together proteins • Each cell contains thousands • Found on reticulum and floating throughout the cell Mitochondria • Mitochondria (like the factory generator): the “power plant” of the cell • Produces energy through chemical reactions – breaking down fats & carbohydrates Golgi Bodies (Apparatus) • Golgi bodies (like the factory packing and shipping department): the UPS or Fed-Ex of the cell • Transports and packages proteins and other materials in the cell – Moves materials within the cell – Moves materials out of the cell Lysosome • Lysosomes (like the factory waste management dpartment): the “wrecking crew” and “trash can” of the cell • Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal • Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes or ruptures Vacuoles • Vacuoles (like factory storage/factory water tower): the “storage container” of the cell • Sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal • Help plants maintain shape- very large in plants Chloroplast (plants only) • Chloroplasts (like factory solar energy plants): turns energy from the sun (with CO2 and water) into food • Contains green chlorophyll • Where photosynthesis takes place Today’s Assignment • Cell Analogy Project (cell structures) How about an example? • Your cell analogy can be a factory, a store, a school, a garage. • You may choose a plant or animal cell • 100 pts possible