* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What Can We See in the Night Sky?
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Coma Berenices wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Open cluster wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
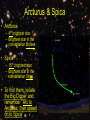
Constellations & Galaxies “The Milky Way has gone a little sour” - Sam Roberts Constellations • Groups of stars that form shapes or patterns – must be officially recognized – if not, the pattern is called an asterism • named after ancient heroes/gods, animals or everyday objects Test Your Knowledge • Q: Is the “Big Dipper” an asterism or constellation • A: Asterism • The big dipper belongs to the constellation Ursa Major (The Big Bear) Ursa Major (The Big Bear) Ursa Minor (The Little Bear) Polaris Polaris Polaris • Find Polaris in the night sky and you can always find North • It is commonly known as “The North Star” • This is merely a geographical coincidence • there is no “South Star” – Sigma Octantis is in the right location but it is so faint to the naked eye that it is useless Arcturus & Spica • Arcturus – 4th brightest star – Brightest star in the constellation Bootes • Spica – 15th brightest star – Brightest star in the constellation Virgo • To find them, locate the Big Dipper and remember “Arc to Arcturus, then speed on to Spica” Orion Cassiopeia Hercules Zodiac Constellations • Form a ring that the Sun seems to pass through each year as the Earth orbits around it. • perhaps the most famous of all constellations because of their use in astrology • There are 13 in total – – – – Aries Taurus Gemini Cancer Leo Virgo Libra Scorpius Pisces Sagittarius Capricornus Aquarius Ophiuchus Cancer (The Crab) Sagittarius (The Archer) Gemini (The Twins) Galaxies • A galaxy is a large collection of gas, dust and hundreds of billions of stars • Earth and the other planets are a part of the Milky Way Galaxy – Appears as a hazy white band in the night sky • Andromeda is the nearest major galaxy The Milky Way Andromeda Types of Galaxies 1. Spiral – have a spiral shape - arms of spiral are mainly gas, dust and bright, young, blue stars 2. Elliptical – shaped like a football - composed of old stars 3. Irregular – no familiar shape NGC 1232 M81 M51 Spiral Galaxies Elliptical Galaxies NGC 5253 M87 Irregular Galaxies NGC 1705 Star Clusters • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band • Globular clusters – Contain 100 000 to 1 million stars arranged in spherical shapes – Do not lie along the band of the Milky Way RCW 108 The Pleiades Open Star Clusters The Pleiades • also known as M45 or the Seven Sisters • located in the constellation of Taurus • dominated by hot, blue stars, which have formed within the last 100 million years. • Of all clusters close to the Earth it is the best known and most striking to the naked eye Harry Potter and the Observable Universe http://astronomyspace.suite101.com/article.cfm/astronomical_names_in_harry_potter