* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answers to those burning questions - 8/2/2012
Survey
Document related concepts
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
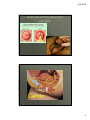
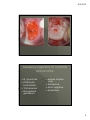
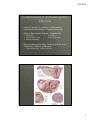
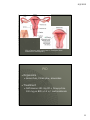
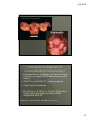
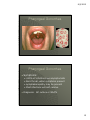
8/2/2012 Answers to those burning questions Ann Avery MD Infectious Diseases Physician-MetroHealth Medical Center Assistant Professor- Case Western Reserve University SOM Medical Director -Cleveland Department of Public Health Basic concepts Transmission dynamics of STDs STDs occur at the intersection of the other epidemics –esp drugs and poverty Condoms work when used consistently Prevention education and behavior change is challenging (to both the provider and the patient) When there’s one, look for others 1 8/2/2012 HIV and STDs Synergy between STDs and HIV ALL clients seeking STD screening should be offered HIV testing at the same time. All patients between 13 and 64 recommended to have HIV test at least once. ( CDC Oct 2006) Risk of an STD Is dependent on: • Personal behaviors • Background Community prevalence • Transmission dynamics of a given STD 2 8/2/2012 Estimates of Risk and Duration risk of Duration acquistion of infectivity Gonorrhea 0.6 10-50 days Chlamydia 0.3 6 mos. Disease HSV-2 0.6 lifelong Chancroid 0.8 20 days HIV-1 0.05 lifelong The Five Ps: Partners Practices Past History of STDs Protection from STDs Prevention of Pregnancy 3 8/2/2012 Urethritis and mucopurulent cervicitis 4 8/2/2012 Causative organisms for Urethritis and cervicitis N. gonorrhea Chlamydia trachomatis Trichomonas Mycoplasma genitalium Herpes simplex virus Adenovirus Gram negative Anaerobes 5 8/2/2012 Diagnostic tests Gram stain Microscopy of the vaginal/ cervical fluid Nucleic acid amplification Culture DNA probes 6 8/2/2012 Complications of Untreated genital infections result of spread of pathogen, inflammatory response and subsequent healing (scarring) Pelvic inflammatory disease / epididymitis • Infertility • Chronic pelvic pain • Ectopic pregnancy prostatitis urethral stricture Disseminated gonorrhea/ reactive arthritis post Chlamydia (Reiter’s syndrome) • Joint involvement, ocular, and skin 7 8/2/2012 Does this cervix have Chlamydia? 8 8/2/2012 CDC 2004 surveillance report Chlamydia rates per 100,000, Cleveland Group 2004-05 Overall 1,029 Black female teens 15-19y 10,341 (1 in 10) Black male teens 15-19y 3,414 (1 in 29) Black females 20-24y 7,985 (1 in 12) Black males 20-24y 4,486 (1 in 22) CDPH Dept of Biostatistics 9 8/2/2012 Why screen and treat an asymptomatic infection? Subtle symptoms Long duration of infectivity Prevent Complications • PID Chronic Pelvic Pain Infertility Ectopic Pregnancy 10 8/2/2012 25% of women with gonorrhea or Chlamydia have endometritis histologically PID Organisms • Gonorrhea, Chlamydia, anaerobes Treatment • Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM + Doxycycline 100 mg po BID x 14 +/- metronidazole 11 8/2/2012 Normal female genitalia How does the diagnosis of Chlamydia affect future fertility? Evaluated time to pregnancy and rates of ectopic pregnancy in relation to CT diagnosis among ALL women 31% CT + and 29.5% CT- became pregnant Time to birth comparable No effect on fertility or ectopic pregnancy noted retrospectively among clients diagnosed with CT Andersen et al. Sex Trans Dis June 2005. 32 (6)377-381 12 8/2/2012 Recurrent Chlamydia infections in young women Prospectively recruited women diagnosed with CT to return for f/u eval at 1 and 4 months ( all treated) Among women negative at first f/u --7.1% positivity at 4 mo f/u Re-screening in 3-4 months recommended for all patients with infection. Whittington et al. Sex Trans Dis Feb 2001. 28(2)117-123 Gonorrhea rates by ethnicity CDC 2007 GISP report 13 8/2/2012 Gonorrhea screening Screening in areas of with at least 1% prevalence • high incidence tend to concentrated in urban areas. NAATs screening Cultures Probes Gonorrhea Can also live in oral pharynx • Usually without symptoms • Easily passed through oral sex to cause urethritis Can live in rectal environment • may cause proctitis or no symptoms 14 8/2/2012 Pharyngeal Gonorrhea Pharyngeal Gonorrhea Symptoms: • >90% of infections are asymptomatic • Sore throat, when symptoms present • Lymphadenopathy may be present • Most infections will self-resolve Diagnosis: GC culture or NAATs 15 8/2/2012 Screening for Rectal and Pharyngeal CT and GC in MSM CDC recommends screening of atrisk men who have sex with men (MSM) at least annually for urethral and rectal GC and CT, and for pharyngeal GC. MMWR, July 9, 2009 STIs in MSM Screened men attending STD clinic and gay men’s health clinic with rectal, pharyngeal and urethral swabs 53% of Chlamydia infections not in urethra 64% of gonococcal infections were not in urethra Kent et al. CID 2005;41:67-74 16 8/2/2012 It’s Everywhere! Kent et al. CID 2005;41:67-74 Asymptomatic infection in Men 86% asymptomatic rectal infections 42% asymptomatic urethral infections Kent et al. CID 2005;41:67-74 17 8/2/2012 Screening for Rectal and Pharyngeal CT and GC The rectum and pharynx are the most common sites of GC and CT infection among MSM. Infections are usually asymptomatic and typically occur without concomitant urethral infection Only a minority of MSM at risk for STDs are screened for GC and CT at the recommended frequency. - treatment same as for urethral infections CDC Recommendations Yearly screening for rectal GC and CT for MSM who had receptive anal intercourse during the preceding year Yearly screening for pharyngeal GC for MSM who have had receptive oral intercourse during the preceding year. Screening is recommended regardless of history of condom use during exposure. 18 8/2/2012 CDC Recommendations Also screen: • at three to sex month intervals for MSM who have multiple or anonymous partners • MSM who have sex in conjunction with illicit drug use, use methamphetamine or whose sex partners have participate in those activities. NAAT Testing Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) is generally more sensitive than culture for the detection of both GC and CT. NAAT tests have not been cleared by the FDA for the diagnosis of extra-genital CT or GC. Under U.S. law, labs may offer NAAT testing for diagnosis of extra-genital CT or GC after internal validation of the method by verification study. 19 8/2/2012 NAAT Testing CDC encourages labs to do their own studies to establish performance and initiate testing. For more information about the process: •Carol Farshy [email protected] NAAT Testing A list of labs that have completed the studies to establish performance is available on the American Public Health Laboratories’ website: www.aphl.org/aphlprograms/infectious.std 20 8/2/2012 21 8/2/2012 FIGURE 2. Percentage of gonorrhea isolates with cefixime MICs ≥0.25 µg/mL and ceftriaxone MICs ≥0.125 µg/mL, by sex of sex partner --- Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project, United States, 2000--2010 MMWR July 8, 2011 / 60(26);873-877 Gonorrhea treatment Ceftriaxone 250 mg or Cefixime 400 mg po – (not for MSM) Plus treatment for Chlamydia Azithromycin 1 gm po once or Doxycycline 100mg po BID x 7 days 22 8/2/2012 Partner Management Maintain abstinence for 7 days while completing treatment regimen and until all partners are treated All sexual contacts within past 60 days should be evaluated and treated Expedited Partner Therapy (e.g. Field delivered Therapy, Patient Delivered Partner Therapy) should be offered if legal NGU Case screnario 33 y/o heterosexual male presents to clinic with dysuria- NGU by gram stain. Treated with doxy 100 BID. Returns in 2 wks and states no relief 23 8/2/2012 NGU Mycoplasma genitalium getting some attention Occurs about 10% of NGU but much higher in pts with “persistent NGU” as relatively resistant to Doxycycline Pearl- responds best to Azithromycin or Moxifloxacin but not Cipro or Levo NGU persistent 24 8/2/2012 Trichomonas Diagnostic options • Wet mount • Culture • Pcr/ naat Treatment issues Trichomonas Single dose Metronidazole is NOT recommended for Bacterial vaginosis due to lower efficacy. 25 8/2/2012 Challenge question Allergy to Metronidazole? Epidemiological Synergy Co-infection with HIV prolongs the infectiousness on STDs STDs facilitate HIV transmission by increasing genital HIV-RNA/DNA levels STDs facilitate HIV acquisition by disrupting epithelial barriers and attracting inflammatory cells GUD increases risk of HIV 8 fold 26 8/2/2012 Urine-Based Tests Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) for gonorrhea and chlamydia Highly accurate Non-invasive collection • High patient acceptability • Appropriate for screening asymptomatic persons Allows screening in nontraditional settings • Community settings • Correctional settings • Schools Urethritis/ cervicitis, proctitis Gonorrhea Chlamydia Trichomonas Mycoplasma, Herpes Simplex Virus adenovirus Vaginitis Trichomonas Bacterial vaginosis Candida Syphilis Herpes Simplex Virus Chancroid (h. ducrei) HPV syphilis Genital ulcers Genital warts 27 8/2/2012 Contact info: Ann Avery MD [email protected] 216 778 7828 office 216 207 1141 pager 28