* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure and function of mitochondria (Slide
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
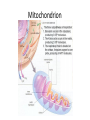
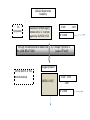
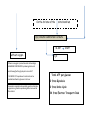
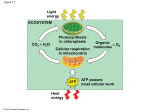
Cellular Respiration 2 Structures and functions Respiration • Three step process: • Glycolysis (all living cells) • Krebs cycle (higher animals) • Electron transport chain (higher animals) Glycolysis = to split sugar Does not need oxygen Occurs in cytoplasm Only releases ¼ of glucose energy C6 sugar = 2 C3 sugars 2 C3 pyruvate Energy captured via 2 ATP H+ released may be captured by NAD in higher cells Catabolic = energy releasing reactions to produce pyruvate from glucose Proteins Carbohydrates Amino acids Glucose Glycolysis Fats Fatty acids Glycerol In cytoplasm Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Mitochondrion Getting into the mitochondrion • Via Link reaction Mitochondrial membrane Release of CO2 3 Carbon Pyruvate Transport protein in the membrane uses ATP 2 Carbon Acetyl coenzyme A • attaches to pyruvate • can be re-used Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Inside the mitochondrion • Where O2 is present, further processing can occur by: – Krebs cycle (in membrane space) – Electron transport chain (on cristae) – Energy requirements of a cell (eg muscle) indicated by: Number of christae Number of mitochondria Krebs cycle • • • • • • • • Needs oxygen Controlled decomposition of pyruvate Releases carbon as CO2 H+ ions captured by NAD Releases 2 ATP Provides > 20 proteins for metabolic processes Refer to p127 in Biozone Look at position on flowchart Electron transport chain • • • • • • • Needs oxygen Located on christae Complex series of reactions Releases energy to give 34 ATP Uses oxidation product of ½ O2 Uses H+ ions from NADH Releases H20 as final product. But what happens when oxygen is not available? • Anaerobic respiration • Is a relatively wasteful process: – In plants it produces toxic wastes like alcohol – In animals lactic acid must be removed to the liver, and converted back to glucose. • Synthesises no more ATP • It does allow the glucose to pyruvate reaction to continue Cellular Respiration Summary In cytoplasm Through the Mitochondrial membrane the LINK REACTION In the matrix of the mitochondrium 2 ADP Glucose (6 carbon sugar) broken into 2 x 3 carbon sugars by GLYCOLYSIS H+ in NAD by Transport protein in (uses ATP ADP) oxygen present KREBS CYCLE 2 ADP 2 ATP 2 ATP H+ in NAD 2 ATP On the christae of the mitochondrium ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN 34 ADP without oxygen 34 ATP H2 O Where no oxygen is present muscle cells undergo ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION producing lactic acid and allowing further glycolysis to occur BUT NO MORE ATP is produced. Lactic acid can be metabolised back to glucose in the liver Anaerobic respiration also used by yeasts and simple organisms eg bacteria producing often toxic wastes like alcohol Total ATP per glucose: 2 from Glycolosis 2 from Krebs Cycle 34 from Electron Transport Chain