* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune System ppt
Survey
Document related concepts
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
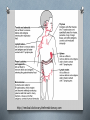
Immune Defenses SBI 4UI Mrs. Tuma What is immunity? What is immunity? O - a variety of white blood cells and proteins that attack foreign invaders such as bacteria and viruses O - immunity is the ability to resist a disease after being exposed to the disease in the past http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com Non-Specific Defenses: -guard against a wide variety of pathogens -does not depend on prior exposure to the pathogen O Skin O Body Secretions e.g.: saliva, tears, stomach acid, urine O Normal flora O White Blood Cells - Natural Killer cells, macrophages, dendritic cells Specific Defenses of the Body: O recognize foreign substances and act to destroy or neutralize them O specific immune defence is a function of Lymphocytes O Two types: - B lymphocytes (B cells): mature in bone marrow - T lymphocytes (T cells): mature in thymus gland O Lymphoid organs - tonsils, appendix, bone marrow, lymphatic system, thymus glands etc. How does it work? [*Antigen = any protein that stimulates an immune response] Pathogen or antigen* Macrophages engulf & display surface antigens stimulates helper T cells cytotoxic T cellls memory T cells Active cytotoxic T cells B Plasma Cells *Make antibodies B Memory cells *Remember how to make antibodies * make cytokines * kill cells via chemical warfare http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100/lectures/immune.htm What about transplantation? Tissue typing - blood types must match (A, B, AB, O) - proteins on cells called (Major Histocompatibility Complex) MHC markers must match closely Rejection - give anti-rejection drugs (a reality!) - some serious side effects What about transplantation? Graft-versus-host disease - seen in bone marrow transplants with leukemia patients - patient's own cells are wiped out by radiation and chemotherapy - transplanted cells start to attack the recipient - try to prevent by closely matching recipients cell protein markers What about vaccination? O weakened/dead form of bacteria/virus or some of its surface proteins O usually injected, but some oral (e.g. polio) O immune system will make antibodies against the antigen and memory cells are stimulated O on second exposure, memory cells can stimulate antibody production very quickly What about vaccination? Examples of Common Vaccines: O DPTP O MMR O Chicken Pox O Meningitis O HPV