* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Subordinate Word Groups Prepositional phrase: begins with a
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
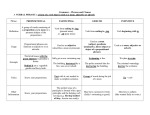
Student Success Center Subordinate Word Groups Prepositional phrase: begins with a preposition (at, by, for, from, in, of, on, to, or with) and usually ends with a noun or noun equivalent; functions as an adjective (nearly always follows the noun or pronoun it modifies) or adverb (can modify a verb, another adverb or an adjective and appear nearly anywhere in a sentence) Verbal phrase: a verb form that does not function as the verb of a clause, including infinitives (the word to plus the base form of a verb), present participles (the -ing form of a verb), and past participles (verb usually ending in -d, -ed, -n, -en, or -t) Participial phrase: always function as adjectives, frequently appear immediately following the noun or pronoun it modifies, and the verbal is either present or past participles Gerund phrase: built around present participles (verb forms ending in -ing), always function as a noun Infinitive phrase: usually constructed around to plus the base form of the verb Appositive phrase: describe nouns or pronouns Absolute phrases: modifies a whole clause or sentence, not just one word Subordinate clauses: patterned like sentences, having subjects and verbs and sometimes objects or compliments, but function as adjectives, adverbs, or nouns (adjective, adverb, or noun clauses) Hacker, Diana, and Nancy Sommers. A Writer’s Reference. 7th ed. Boston: Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2011. Print