* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of Speech, Phrases, and Clauses
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Agglutination wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Untranslatability wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Contraction (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
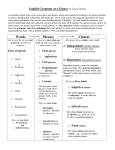
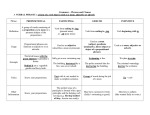
Parts of Speech Words in the English language are divided up into eight categories called parts of speech based on their function. The eight parts of speech are Noun—person, place, thing, or idea Pronoun—a word that takes the place of a noun Adjective—a word that describes a noun or pronoun Verb—an action word Adverb—a word that describes a verb, adjective or other adverb Conjunction—a word that links words, phrases, or clauses together Preposition—a word that describes position Interjection—a word that is uttered in surprise or pain The parts of speech in action In the following sentence, the parts of speech are labeled: James ran down the street and waved his arms frantically. Green=Noun Orange=Verb Preposition=Blue Conjunction=Red Pronoun=Black Adverb=Aqua Olive Green=article (a form of adjective) Why is this Important for Writing? Knowing the parts of speech tends to give us terminology that helps us describe parts of the language, so we can describe how it works and what types of mistakes are frequently made (for example subject/verb agreement errors). Phrases: Phrases are groups of words, but are not complete sentences. There are a few types of phrases in English two of which are Prepositional phrase: this phrase starts with a preposition and ends with a noun (for example “under the bed”) Verb phrase: This phrase consists of verbs, frequently a main verb and a helping verb (for example “had read”) We use phrases to help us describe the function of groups of words that are parts of a sentence. Clauses A clause is a group of words that have a subject and a verb. There are two types of clauses in English: Dependent (the clause cannot stand on its own as a sentence) Independent (the clause can stand on its own as a sentence) Dependent clause example: “Because it rained” Independent clause example: “I kicked the ball” Clauses continued The English language connects clauses together to form more sophisticated sentences. As you study this, you will run into the four sentence types: Simple Compound Complex Compound Complex Some errors are created by not joining clauses together correctly to create these types of sentences. Examples of Sentence Types: Simple Sentence: I drove home. Compound Sentence: I drove home, and I cleaned the garage. Complex sentence: Because I brought my umbrella, I won’t get wet walking home. Compound Complex: Because I brought my umbrella, I won’t get wet walking home, and I won’t catch cold.