* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lect19cut
Survey
Document related concepts
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Fauna of Africa wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
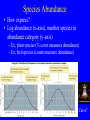
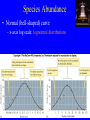
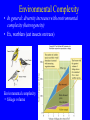
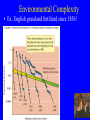
Species abundance and diversity (Ch. 16) New Unit: Communities/Ecosystems • Community: Interacting species in defined area. • Functional groups: subdivide organisms based on life history – Guild: Organisms living in same fashion • Animal Ex.: granivore guild Harvester ants K-rat New Unit: Communities/Ecosystems • Growth form: Combination structure + growth pattern. • Ex.: tree, shrub, graminoid, forb, climber Species Abundance • How express? • Log abundance (x-axis), number species in abundance category (y-axis) – Ex, plant species (% cover measures abundance) – Ex, bird species (counts measure abundance) Curve? Species Abundance • Normal (bell-shaped) curve – x-axis log scale: lognormal distributions Species Abundance • Often only part curve seen. – Why? Sample size. • Ex, moth community & sample size Tiger moth (Arctiidae) Sphingid moth (Sphingidae) Species Diversity • Two factors: – 1) Species Richness • Number species Species Diversity • Two factors: – 2) Species Evenness • Relative abundance of species Species Diversity • How integrate? • Diversity Index. Gives single number Species Diversity • Common: Shannon Wiener Index – Fish diversity lab! Ecology SU 2005 Species Diversity • Shannon Wiener Index: s H´ = - pi logepi i=l • • • • H´ = Value of index pi = Proportion individuals of ith species loge = Natural log S = Number species in community Species Diversity • Ex: b greater diversity (same richness) Rank Abundance Curves • Rank abundance curves: – Relative abundance (proportional abundance: y-axis, log scale) vs. abundance rank (x-axis) • a vs. b Rank Abundance Curves • Ex: reef fish communities (Gulf of California) Rank Abundance Curves • Which more diverse? (Richness, evenness) Environmental Complexity • In general: diversity increases with environmental complexity (heterogeneity) • Ex, warblers (eat insects on trees) Environmental complexity = foliage volume Environmental Complexity • Foliage height diversity correlates positively bird species diversity Environmental Complexity • Hutchinson (1961): – Phytoplankton: simple environments, compete same nutrients – But many species coexist Environmental Complexity • Algal niches. – Ex, Diatoms (Protists, Phylum Bacillariophyta) – Photosynthetic – Cell walls: silicate Environmental Complexity • Coexistence depends on ratio silicate:phosphate • Different niches: different diatoms dominate Environmental Complexity • Do nutrients vary in “real world?” • Ex, Pyramid Lake, Nevada Environmental Complexity • Ex, Pyramid Lake, Nevada Environmental Complexity • Tropical rain forest diversity? • Amazon: 1 hectare (2.47 acres) up to 750 tree species USA has 850 native tree species! Environmental Complexity • Diversity due to: – 1) many species per community – 2) many communities per unit area • Complexity helps explain diversity Environmental Complexity • Relationship nutrients and rainforest richness? – Negative! – Competitive exclusion by best competitors Environmental Complexity • Reducing environmental complexity – When humans add nutrients (intentionally or not!) • Reduces diversity – Reduces limiting nutrients Environmental Complexity • Ex, English grassland fertilized since 1856! Environmental Complexity • Ex, N fertilization & ectomycorrhizal fungi diversity – N aerial pollutant (Alaska factory) Environmental Complexity • Contributes to diversity • But so does…disturbance • Define?? Disturbance and Diversity • Disturbance: departure from “average?” • Sousa: – Discrete, punctuated, killing, displacement, or damaging of individuals that directly or indirectly creates an opportunity for new individuals to establish. • White and Pickett: – Relatively discrete event that disrupts ecosystem, community, or population structure and changes resources, substrate availability, or physical environment. Disturbance and Diversity • Two major characteristics: – Frequency (how often) – Intensity (how severe) • Abiotic: fire, hurricanes, ice storms, flash floods • Biotic: disease, predation, humans Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis Intermediate Disturbance • Ex: intertidal zone – Disturbance depends on boulder size. Intermediate Disturbance • Richness greater medium boulders Temperate Grasslands • American prairie dog disturbance…. Disturbance Disturbance • Prairie dog control: reduced populations 98% Humans as disturbance • Human disturbance & diversity – Ex, chalk grasslands (Europe) – Graze livestock, cut hay – What happened when “protected”? Humans as a disturbance • Diversity dropped (Brachypodium dominated)