* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sc9 - a 2.2(teacher notes)
Survey
Document related concepts
Reproductive suppression wikipedia , lookup
Parental investment wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Parthenogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Animal sexual behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
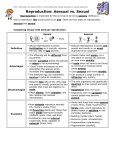
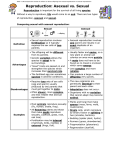
Learning outcomes: 1 I can distinguish between asexual and sexual reproduction. 2 I can describe examples of each type of reproduction. 2.2 . Asexual and Sexual Reproduction involves only one parent. All of the offspring are identical to the parent. There are different types of asexual reproduction: Binary Fission – only single-celled organisms reproduce in this way. The cell splits into two cells and each one is identical. Budding – the parent organism produces a bud (a smaller version of itself), which eventually detaches itself from the parent and becomes a selfsufficient individual - identical to the parent. Coral also reproduces in this way, but do not detach themselves Spore Production – spores are similar to seeds, but are produced by the division of cells on the parent, not by the union of two cells. One parent may produce many spores, each of which will grow into a new individual, identical to its parent. Vegetative Reproduction – is the reproduction of a plant not involving a seed, including; cuttings, runners, suckers, tubers. Which is which??? _________________________ __________________________ __________________________ _________________________ Usually involves two organisms. The offspring have a mix of characteristics: half from each parent. Gametes are essential for sexual reproduction: reproductive cells that have one role – to join with another during reproduction. o Ex: sperm and Egg are gametes *** This is super important to know. Male gametes = sperm cells. Female gametes = egg cell. During mating, the SPERM CELL and EGG CELL unite. This creates one entity, the ZYGOTE. The zygote is the first complete cell of the individual. Each and every cell will be then be duplicated by splitting in half: the size of each cell stays the same. (we call this process of duplication: MITOSIS) These cells duplicate until an EMBRYO is developed. The EMBRYO then continues to then develop into a FOETUS. *** This is super important to know. Like animals, plants reproduce thanks to male and female gametes uniting. Except most plants contain both male gametes and female gametes. Only a few plants have one or another. Like animals, these gametes unite, during FERTILIZATION, to form a ZYGOTE that then develops into an EMBRYO. Pollen = male gametes. These are located on the STAMEN. Ovules = female gametes. These are located on the PISTIL. Cross-pollination occurs when pollen from one plant is carried to the stigma of another plant by wind, water or animals (bees or butterflies). Asexual (advantages): Reproduce very quickly Can build population very quickly (bacteria) Asexual (disadvantages): When the environment changes, they all die if cannot adapt. Sexual (advantages): Provides lots of variation. This variation means the populations can survive when the environment changes. Sexual (disadvantages): It takes a lot of energy to reproduce. It takes a lot of time. This makes the populations much, much smaller Online Activity: comparing asexual and sexual reproduction Graph analysis 1. What is the subject? 2. What conclusion can be made with this diagram? 3. What can be inferred by this diagram? > Create a visual diagram of either: - Asexual reproduction methods - Sexual reproduction for plants - Sexual reproduction for animals. Diagram must include Visual diagram that explains the concept and brief explanation paragraph at bottom of page. Optional (But great review for exam): Venn diagram or table that compares advantages and disadvantages of both Sexual and Asexual reproduction. Optional: Questions from page 36 and 37 Exam on Unit A section 1.1 – 2.2