* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics Review
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
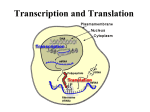
DNA: genes on chromosomes DNA is composed of nucleotides A Nucleotide has: - Deoxyribose Sugar - Phosphate - Nitrogen Base Adenine Thymine Guanine Cytosine A - T and G - C DNA is a helix molecule Hydrogen bonds are in between the bases. Note the nucleotides pairing. DNA self replicates before cell division 5’ 3’ The DNA strand opens and will add nucleotides. A to T and G to C. C A G T One strand grows continuously, the other grows discontinuously. Enzymes join the strands. 3’ 5’ DNA produces proteins in two steps Transcription: mRNA production Translation: protein production Transcription is when the mRNA produced. mRNA from DNA as expected…….. GGG CCC TTT AAA CCC GGG AAA UUU The bases of the DNA are matched up with the RNA bases A-U, T-A, G-C, C-G AAA TTT GGG CCC GGG CCC TAA UUU AAACCC GGG CCC GGG AUU Synthesis starts at the beginning of a gene Transcription moves in a 5’ to 3’ direction Transcription finishes as mRNA is released The DNA triplets help code for amino acids during translation because DNA is in control of the triplets of mRNA (the codon). The anticodon of the tRNA matches this codon on the ribosome and brings with it an amino acid. UUU AAACCC GGG CCC GGG AUU AAA UUU GGG CCC GGG CCC UAA | | | | | | | Phe Lys Pro Gly Pro Gly Ile Bonds form between amino acids When the chain is complete, a new protein has been formed. Video of Protein Synthesis. On the ribosome mRNA codons match tRNA anticodons linking amino acids Steps to Protein Synthesis • Transcription: Production of mRNA by DNA in nucleus. Base pairs match up A to U and G to C (RNA has no Thymine). • Translation: In the cytoplasm, on the ribosome, the mRNA codon matches tRNA anticodon to bring the proper amino acid in for bonding. Once the whole mRNA is read by the ribosome, the stop codon ends the production of the peptide chain; the protein is complete! How is RNA different than DNA? •Ribose Sugar •Uracil for Thymine •Single strand •not self replicating •found all over the cell • Nucleolus - Site of ribosome production • Nucleus - location of DNA, cell organizer • Chromosomes - coiled chromatin • Chromatin - DNA and proteins not coiled • DNA - helix shaped molecule with base sequences that make up the genetic code • RNA - made by DNA, assists DNA to make proteins as a messenger (mRNA), transfer molecule (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). END!