* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Long-term potentiation wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Dendritic spine wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic noise wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
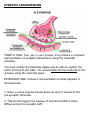
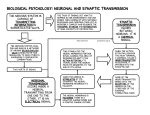
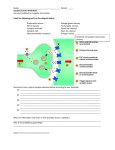
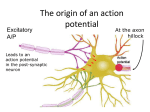
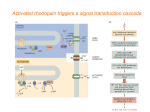
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION TODAY’S TASK: Your job, in your groups, is to produce a complete representation of synaptic transmission using the materials provided. You must include the following stages and be able to explain the entire process to the class. You should label the key features of the synapse using the coloured paper. EXTENSION TASK: include a representation of what happens in schizophrenia. 1. When a nerve impulse travels down an axon it arrives at the pre-synaptic terminals. 2. This arrival triggers the release of neurotransmitters which diffuse across the synaptic cleft. 3. When released, the neurotransmitter must be taken up immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft thus making it inactive. 4. If successfully transmitted, the nerve impulse is then carried along the post-synaptic neuron until it reaches the next synaptic terminal where the message will continue to pass on via electrical impulses. KEY TERMS Synapse: the gap between the end of one neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron. Neurotransmitter: a chemical substance released from a synaptic vesicle that affects the transfer of an impulse to another nerve or muscle. Synaptic transmission: Additional Information Neurotransmitters include: dopamine, acetylcholine and serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, for example, is a mental disorder thought to be the result of excessive activity of the neurotransmitter dopamine. This means that neurons which respond to dopamine fire too often (they are too excitatory) and transfer too many messages through the brain as a result. When this happens symptoms of schizophrenia start to occur. These symptoms can be controlled with anti-psychotic drugs e.g. chlorpromazine, which are designed to block the receptor sites for dopamine.