* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Analogous Structures
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
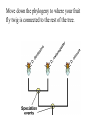
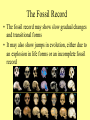
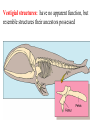
What is species? Species: a group of individuals that look similar and whose members are capable of producing fertile offspring in the natural environment Tree of Life These happy face spiders look different, but since they can _________, they are considered the same species: Theridion grallator A.) Dance B.) Interbreed C.) Spin a web D.) Eat bugs Speciation A lineage-splitting event that produces two or more separate species. Imagine that you are looking at a tip of the tree of life that constitutes a species of fruit fly. Move down the phylogeny to where your fruit fly twig is connected to the rest of the tree. That branching point, and every other branching point on the tree, is a speciation event. At that point genetic changes resulted in two separate fruit fly lineages, where previously there had just been one lineage. How do new species arise? Would polar bear evolution create a new species? Why or why not? Here is one scenario that exemplifies how speciation can happen: The scene: a population of wild fruit flies minding its own business on several bunches of rotting bananas, cheerfully laying their eggs in the mushy fruit... Disaster strikes: A hurricane washes the bananas and the immature fruit flies they contain out to sea. The banana bunch eventually washes up on an island off the coast of the mainland. The fruit flies mature and emerge from their slimy nursery onto the lonely island. At this point, speciation has not occurred — any fruit flies that got back to the mainland could mate and produce healthy offspring with the mainland flies. The populations diverge: Ecological conditions are slightly different on the island, and the island population evolves under different selective pressures and experiences different random events than the mainland population does. Morphology, food preferences, and courtship displays change over the course of many generations of natural selection. So we meet again: When another storm reintroduces the island flies to the mainland, they will not readily mate with the mainland flies since they've evolved different courtship behaviors. The few that do mate with the mainland flies, produce inviable eggs because of other genetic differences between the two populations. The lineage has split now that genes cannot flow between the populations. Differing selection pressures on the two islands can complete the differentiation of the new species. EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION Comes from many disciplines! 1. 2. 3. 4. Fossils Anatomy Embryology Biochemistry Fossils tell a story… The Evidence for Evolution Why is the fossil record incomplete? – Only hard parts become fossilized. – Not all organisms die in the right conditions for fossilization – Not all fossils have been discovered Does this falsify evolution?! Whale Evolution The Fossil Record • The fossil record may show slow gradual changes and transitional forms • It may also show jumps in evolution, either due to an explosion in life forms or an incomplete fossil record We found the fossil — no joke! Land Mammal ? ? ? Complete series of transitional fossils Ocean Mammal ? Evolution from sea to land 2006 fossil discovery of early tetrapod 4 limbs Missing link from sea to land animals Evolution of birds Today’s organisms descended from ancestral species Fossil of Archaeopteryx • lived about 150 mya • links reptiles & birds claws wing-like forelimbs teeth thin ribs long tail feathers Replica of Archaeopteryx fossil; half bird half reptile Reptile-like features Bird-like features Other Evidence for Evolution • Comparative Anatomy – Examining differences and similarities in structures – Homologous structures – same structure, different purpose – Analogous Structures – different structures, same purpose – Vestigial Structures – non-functioning structures that probably had a function in the past. Homologous Structures Related organisms will share similarities that are derived from common ancestors. Similar characteristics due to relatedness are known as homologies. But don’t be fooled by these… – look similar • on the outside – same function – different structure & development • on the inside – different origin Analogous Structures The clue to common descent is common structure, not common function. A bird’s wing and a horse’s front limb have different functions but similar structures. Body parts that share a common function, but not structure, are called analogous structures. The wing of a bee and the wing of a bird are analogous structures. Convergent evolution 3 groups with wings – Does this mean they have a recent common ancestor? Convergent evolution The independent development of similar structures in organisms that are not directly related. Convergent evolution is usually seen in animals and plants that live in similar environments Convergent Evolution Convergence among fast-swimming predators Divergent evolution describes evolution toward different traits in closely related species. red fox kit fox ancestor Vestigial structures: have no apparent function, but resemble structures their ancestors possessed 30 Adaptation Lab • Using what you have learned, apply your knowledge to the lab! Misconception: “Evolution is a theory about the origin of life.” Evolutionary theory deals mainly with how life changed after its origin. Misconception: “Evolution is like a climb up a ladder of progress; organisms are always getting better.” It is true that natural selection weeds out individuals that are unfit in a particular situation, but for evolution, “good enough” is good enough. No organism has to be perfect. Misconception: “Evolution means that life changed ‘by chance.’ ” • Chance is certainly a factor in evolution, but there are also non-random evolutionary mechanisms. Random mutation is the ultimate source of genetic variation, however natural selection, the process by which some variants survive and others do not, is not random. What Do You Know About Evolution? In a population of antelopes that live on the plains with a large number of cheetahs (fast predators of antelopes), which of the following is NOT true: A. Individual antelopes will develop genes for speed in order to survive. B. Those antelope who are faster are likely to survive better. C. Those antelope who have the most fertile offspring would be considered to be biologically successful. D. Some antelopes will be killed by cheetahs. Which of the following concepts is NOT a part of evolutionary theory: A. There are limited resources available to an organism. B. Organisms will pass on characteristics that they develop during their lives to their offspring. C. Traits are passed on to offspring via DNA. D. Inherited traits may change over time in a population of organisms. Within a given species: A. There is often a great deal of variation. B. Normally only very little variation. C. There is an individual or several individuals that we can say are “normal.” D. Variation is only something that is visible, not hidden. The following is a good example of biological adaptation: • It’s cold, so you put on a jacket. • Your puppy stops urinating inside after you scold it when it does. • A strain of Stapholococcus bacteria appears that is not killed by a dose of antibiotic that normally kills these bacteria. • As a young man, you believe that females prefer well-muscled males, so you start working out. In evolutionary terms, the “fittest” in the phrase “survival of the fittest” means: A. Those organisms that produce the most fertile offspring. B. Strongest. C. Fastest. D. Best able to adapt to the environment. The theory of evolution by natural selection was developed most famously by: A. B. C. D. Gregor Mendel Watson and Crick Charles Darwin Rosalind Franklin The picture most clearly shows evidence for which of the following? A. Certain birds choose to develop particular beak shapes. B. No relationship between function and form. C. Evolution has probably occurred among a group of birds. D. Survival of the fittest. Biology teaches all of the following EXCEPT: A. Life began billions of years ago. B. The first life was single celled. C. Evolution of life has generally progressed from simple life forms to more complex ones. D. Life began with many complex animals arising at about the same time. Thousands of years ago, giraffes with short necks were common within giraffe populations. Nearly all giraffe populations today have long necks. This difference could be due to: A. Giraffes stretching their necks to keep their heads out of reach of predators. B. Giraffes stretching their necks so they could reach higher food in the trees. C. A mutation in genetic material controlling neck size in some skin cells of a giraffe. D. A mutation in genetic material controlling neck size occurring in the reproductive cells of a giraffe. Scientists have concluded that snakes evolved from ancestors with legs. Which of the following statements provides best evidence for this conclusion? A. Most species of snakes live on land. B. Snakes move extremely fast to catch prey. C. Snakes have a well-developed backbone and muscular system. D. Some species of snakes have limb buds during their embryonic development. Which of the following best explains how the fossil record provides evidence that evolution has occurred? A. It indicates that forms of life existed on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago. B. It indicates the exact cause of structural and behavioral adaptations of organisms. C. It shows how the embryos of many different vertebrate species are very similar. D. It shows that the form and structure of groups of organisms have changed over time. Evolution is: A. A theory, and therefore not strongly supported. B. Not observable or testable. C. A process that explains patterns that can be observed in nature. D. Undoubtedly true. Evolution produces organisms that: A. Are better adapted to a particular environment than the ones they evolved from. B. Are physically stronger than the ones that they evolved from. C. Are more complex than the ones they evolved from. D. More common than the ones they evolved from. During the development of humans, which of the following is true? A. A new variation in an individual is a sign of evolution. B. The same variation spread through a population is a sign of evolution. C. Certain individuals, if they have a useful enough adaptation, can evolve. D. The first person who was born with blue eyes can be said to have evolved. Mutations may: A. Have positive effects B. Have negative effects C. Have no effect Variation comes about in all of the following ways EXCEPT: A. So an organism can be more successful in its environment. B. Through shuffling of genes between organisms C. Because of mutations D. Randomly