* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
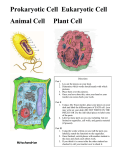
Three (3) Tries: Eukaryotic Cell Structure and Function Name _________________________________________________________ Date _____________ Pd _______ Student A: Ask your partner to give the organelle that matches the organelle structure description. Organelle Organelle Structure 1st Try 2nd Try (3 pts) 1. nucleolus 2. cytoplasm 3. smooth ER 4. chromatin 5. Golgi apparatus 6. nucleus 7. chloroplast 8. plasma membrane (cell membrane) 9. ER 10. central vacuole 11. cilia 12. cell wall 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. lysosome chlorophyll rough ER cytoskeleton flagella ribosome The organelle found inside the nucleus. The interior of the cell including the clear, gelatinous fluid (cytosol). An organelle with a series of highly folded membranes, with no ribosomes. Long, tangled strands of genetic material (DNA). An organelle with a system of flattened tubular membranes. The central membrane-bound organelle surrounded by a double membrane. Surrounded by a pair of membranes, with stacks of flattened disks inside. Composed of a double layer membrane (phospholipid bilayer) that covers a cell’s surface. Organelle with a highly folded inner membrane. In plant cells, a large fluid filled vesicle in the cytoplasm. Short hair-like projections composed of microtubules. A firm, rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plant cells, fungi cells, most bacteria, and some protists. Vesicles that contain digestive enzymes. Green pigment found in chloroplasts. An organelle with a series of highly folded membranes, covered in ribosomes. A web of various protein fibers. Long, hair-like projections found on some cell surfaces. A non-membrane bound organelle. Total Points Earned: __________________ (2 pts) 3rd Try (1 pt) Three (3) Tries: Eukaryotic Cell Structure and Function Name _________________________________________________________ Date _____________ Pd _______ Student B: Ask your partner to give the organelle that matches the organelle function description. Organelle Organelle Function 1st Try 2nd Try (3 pts) 1. cytoskeleton 2. ER 3. cell wall 4. flagella 5. chloroplast 6. chlorophyll 7. cytoplasm 8. vacuole 9. nucleus 10. ribosome 11. lysosome 12. plasma membrane (cell membrane) 13. nucleolus 14. smooth ER 15. chromatin 16. rough ER 17. mitochondria 18. cilia Supports the cell in the same way that bones support your body. Modifies, sorts and packages proteins and other materials to be transported out of the cell Provides support and protection for plant cells, fungi cells, bacteria & some protists. Move cells using a whip-like motion. Absorbs light energy and chemically creates sugars (Photosynthesis). Pigment required for photosynthesis to occur. Suspends the cell’s organelles and is the site of numerous chemical reactions. Used for temporary storage of water, ions (charged particles), nutrients and wastes. Manages cellular functions and contains DNA. Where proteins and enzymes are made. Digest excess or worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria. Acts as a barrier between the inside of a cell and the cell’s environment. Controls what goes into and out of the cell. Makes ribosomes. Makes lipids and breaks down toxic substances. Contains the instructions for making proteins. Packages proteins made by the ribosomes into vesicles. The site of cellular respiration (turning food energy into ATP) Help with movement and feeding. Total Points Earned: __________________ (2 pts) 3rd Try (1 pt) Three (3) Tries: Eukaryotic Cell Structure and Function Name _________________________________________________________ Date _____________ Pd _______