* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 15-4 Secession and War
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
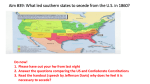
Secession and War 15-4 Objectives • Learn how the 1860 election led to the breakup of the Union. • Learn why secession led to Civil War. 1860 Election In 1860, the primary issue would be slavery. It had ripped apart the Democratic Party, and was on the brink of destroying the nation. Four candidates emerged. Stephen Douglas The Northern Democrats chose the Illinois senator who backed popular sovereignty. John C. Breckinridge The Southern Democrats choice was a Kentuckian who supported slavery and the Dred Scott Decision. John Bell The Constitution Union Party, moderates from the north and south, nominated John Bell of Tennessee. Abraham Lincoln Allowing slavery where it already existed, but oppossing its expansion, Republicans nominated Abraham Lincoln. Election Results On November 6, 1860, Lincoln wins 18 states, 180 of 303 electoral votes, despite his name not being on the ballot in 11 southern states. Secession The election results clearly showed how the south now knew they could be out voted by the north. Talk of secession began to increase. On December 20, South Carolina held a convention and voted to secede from the Union. More States Secede Not long after South Carolina seceded, they were joined by Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. Confederate States of America On February 4, 1861, delegates from the seceding states met in Montgomery Alabama, form a new country. Jefferson Davis Jefferson Davis, Senator from Mississippi is chosen as President. Alexander Stevens from Georgia selected as Vice President. Confederate Actions Believing that all government property belonged to the states that had seceded, the South began to sieze various instillations such as forts, post offices, government buildings. Lame Duck While this was happening, Buchanan did nothing. He was waiting to let Lincoln handle these issues. Fort Sumter One of the last posts held by the North was Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina. Robert Anderson Major Robert Anderson, from Kentucky, was sent to command the garrison. P. G. T. Beauregard Commanding the Southern forces was Pierre Gustav Toutant Beauregard, a former student of Anderson’s. War After weeks of tension, the shooting war began on April 12, 1861 at 4:30 am. Surrender After 33 hours of bombardment, Anderson surrenders. Lincoln’s Reaction On April 15, Lincoln declares an “insurrection” and calls for 75,000 volunteers. Upper South Secedes Outraged at the thought of Northern troops marching across their states, the upper South states of North Carolina, Arkansas, and Tennessee secede. Days later, Virginia secedes. War On April 29, the Confederate States declare war on the United States.