* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download here - iGEM 2015
Survey
Document related concepts
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
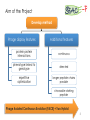
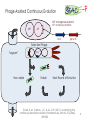
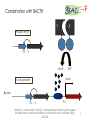
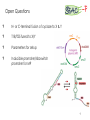
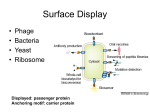
BIOTEChnologisches Zentrum iGEM 2015: Evolution through time and SPACE-P The adaptation and connection of PACE, BACTH and Affibodies to the new project, Structural Phage Assisted Continuous Evolution of Proteins Bo Heinz, Bastian Joffroy 01/06/2015 Motivation from Phage Display Diversity phage display: 108-109 All possibilities for ~ 7 aa Directed (207=1.3×109) Continuous Iterative binding washing amplification further analysis elution www.wikimedia.org 2 Aim of the Project Develop method Phage display features Additional features protein protein interactions continuous phenotype linked to genotype directed repetitive optimization longer peptide chains possible choosable starting peptide Phage Assisted Continuous Evolution (PACE) + Two Hybrid 3 Phage Assisted Continuous Evolution MP: mutagenesis plasmid AP: accessory plasmid MP AP lock gene III Selection Phage key‘ “Lagoon” Non-viable Viable Next Round of Evolution Esvelt, K. M., Carlson, J. C., & Liu, D. R. (2011). A system for the continuous directed evolution of biomolecules. Nature, 472(7344), 499-503. 4 Combination with BACTH Y X Phage vector T18 - Y cAMP ATP pLac E. coli genome ΔcyaA T25 - X P3 Battesti, A., & Bouveret, E. (2012). The bacterial two-hybrid system based on adenylate cyclase reconstitution in Escherichia coli. Methods, 58(4), 325-334. 5 X & Y Choice Y: Scaffold protein – affibody • • • highly stable core variable regions no disulfide bridges long-term goal X: human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER2) • • established positive control of scientific interest replacement of antibodies Eigenbrot, C., Ultsch, M., Dubnovitsky, A., Abrahmsén, L., & Härd, T. (2010). Structural basis for high-affinity HER2 receptor binding by an engineered protein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107(34), 15039-15044. 6 Planned Setup 7 Conclusion SPACE-P is a simple tool that aims to enhance the development and detection of proteinprotein interactions. The System combines methods from both PACE and BACTH. This method has promising applications to develop new affibodies for targeting epitopes of interest. It may be a potential replacement for currently less efficient techniques used in drug discovery and research. 8 Open Questions ? N- or C-terminal fusion of cyclase to X & Y ? T18/T25 fused to X/Y ? Parameters for setup ? Inducible promoter/riboswitch promoter for MP 9