* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membrane Lab Day #2
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
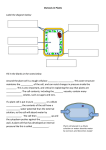
Biology Cell Unit Homework Packet #3 Name DUE: HW #5 Egg Demo HW #6 Elodea lab HW #7 Cell Membrane and Transport HW #8 Hour Drawings Analysis ____ ____ Drawings Analysis ____ ____ Questions ____ Questions ____ _______ / 5 possible points Homework #5: Egg Demonstration An egg can be used to further demonstrate the properties of cell membranes. We will start this demonstration with an egg that has been soaked in vinegar. We will place the egg in syrup tonight, and then transfer the egg to water the following night. Be sure to make accurate drawings of the egg each day. Egg in vinegar Egg in syrup Egg in water Analysis and Conclusions Answer the following questions on the lined pages provided using complete sentences. I will be really impressed if you use what you know about cells and cell parts to answer them. A. What did the vinegar do to the egg? Why was it important to put the egg in the vinegar before placing it in any other solution? Vinegar reacted with calcium carbonate in egg shell and dissolved it leaving only membrane surrounding egg. B. Use your knowledge of osmosis to explain what happened to the egg in syrup. There is a greater concentration of water inside the egg than in the syrup. When egg is placed in syrup, water leaves the egg (moves from high to low concentration) making the egg shrivel. C. Use your knowledge of osmosis to explain what happened to the egg in water. When egg is place in water, concentration of water is higher outside the egg than inside. Water flows into the egg, making the egg expand. D. Describe a potential source of error in this lab. How might you design the experiment to reduce or eliminate this error? Answers will vary Homework #6: Elodea Lab Background: Eukaryotic cells are comprised of a cell membrane and many individual cell parts (organelles) that are each surrounded by their own membrane. These membranes keep the functions of the cell parts separated and more efficient. Materials must be passed through these membranes and delivered through each of the cell parts. Today we will observe some organelles and observe water loss (by osmosis) from a plant cell, Elodea. This process is also known as PLASMOLYSIS. Procedure: Part A: 1. Pick one leaf of Elodea, place in a drop of water on a microscope slide. Cover with a cover slip. 2. Observe cells using medium or high power. I find it easier to use medium for this lab, but you can use high power if you can distinguish individual cells. Each of the “bricks” that you cell is a cell and the green dots are chloroplasts. Draw one typical cell and please label: cell membrane, cytoplasm, chloroplasts and cell wall. PAY SPECIAL ATTENTION TOTHE LOCATION OF THE CHLOROPLASTS!!!! They are either scattered all over the inside of each cell or clustered in the center of each cell. Which objective did you use? Calculate the magnification: What type of cell? plant Part B: Inducing Plasmolysis in Elodea using high concentration salt water. 1. Bring your slide back to the front. Add one drop of 6% salt. 2. Again, draw one typical cell and please label: cell membrane, cytoplasm, chloroplasts and cell wall. PAY SPECIAL ATTENTION TO THE LOCATION OF THE CHLOROPLASTS!!!! They are either all over the inside of the cell or clustered in the center of the cell. Elodea in salt water Post-Lab Questions: Additional Information: Tap water is typically 1% salt and 99% water. Our 6% salt water is only 94% water and 6% salt. Cells are usually 98% water and 2% salt. 1. Add arrows to both drawings of Elodea showing the direction water molecules are moving. Arrows should show water molecules moving out of Elodea. 2. Why is water moving in that direction? What is this process called? Water moves from high to low concentration across a membrane through the process of osmosis. Did the Elodea leaf cell wall change shape in the salt water? Why or why not? Cell wall does not change shape. Cell wall is rigid and permeable to both salt and water. Homework #7 Membrane Investigation: Osmosis can be a difficult concept to understand especially because it is hard to see happening in living cells that are far too small for us to see without using microscopes. However, we can use an artificial membrane that has many of the same properties of cell membranes. This artificial membrane, called “dialysis tubing”, allows us to do some important experiments to study osmosis. Like a cell membrane, dialysis tubing is “selectively permeable” – it has extremely tiny holes that allow small molecules to pass through the membrane while molecules larger than the holes are trapped. In this experiment we are going to make some predictions about the direction of osmosis using starch and dialysis tubing. Some important factual information first: - Osmosis is the diffusion of water from areas of high water concentration to areas of low water concentration. - Starch is a large molecule consisting of many sugar molecules hooked together. It is too large to pass through the tiny holes in the dialysis tubing. - Starch and iodine combine to create a dark purple-black color. Cell Membrane Lab Day #1 Acts as the “gatekeeper”. Determines 1. What is the role of a cell membrane? what goes into and out of cell. 2. What would the solution within this model represent? cytoplasm of the cell. The solution represents the __________ 3. Record the following information about the experimental setups for Day 1: A. 90% water 1. 98% water B. 10% starch 2. 2% iodine Day 1 A. B. 1. 2. Color of Liquid In Beaker Mass of Tubing Color of Liquid in Tubing Beaker 1 Day 2 A. 98% water 1. 90% water B. 2% iodine 2. 10% starch Day 1 A. B. 1. 2. Day 2 Color of Liquid In Beaker Mass of Tubing Color of Liquid in Tubing Beaker 2 A. 98% water 1. 98% water B. 2% iodine 2. 2% iodine Day 1 A. B. 1. 2. Beaker 3 Color of Liquid In Beaker Mass of Tubing Color of Liquid in Tubing Day 2 Predictions 4. The beakers and tubing will be stored overnight. Using your knowledge of osmosis, predict what we will see tomorrow. Color of liquid in tubing Color of liquid in beaker Mass of tubing Beaker #1 Beaker #2 Beaker #3 Cell Membrane Lab Day #2 5. Record your observations for Day 2 next to EACH of the diagrams. 6. For each beaker, use arrows to clearly show which direction each molecule moved. Results 7. Develop a BAR graph that shows the how the mass of the tubing (Y-axis) changed over time (xaxis) for each beaker. Be sure to include a title, key, and labeled axis (X and Y) on your graph. Neatness counts. Cell Membrane Investigation Analysis and Conclusions Answer the following questions using complete sentences. E. What cell process was demonstrated by Beaker #1? The cell process demonstrated by Beaker #1 was osmosis. F. What direction did the iodine move? How do you know? The iodine moved out of the tubing. We were able to determine this because the liquid in the beaker turned purple. G. Place the following items in order from largest to smallest: the size of the holes in the tubing, iodine, starch. The largest was the starch. Then the holes in the tubing. Finally, the smallest was the iodine. Homework #8 – Questions: 1. Using pictures, illustrate what is meant by the term “selectively permeable”. Then write a definition using your own words. Answers will vary. 2. Using the terms concentration and equilibrium write one sentence that defines “diffusion”. Answers will vary. Should be similar to: “Diffusion is the random movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached. 3. Below are examples of two typical cells – an animal cell and a plant cell. Remember, starch is much too big to fit through the cell membrane. Salt is also too big. Draw the appropriate arrows for water and the final result. The first example is an animal cell and the second is a plant cell. 90% water 80% water 10% salt 20% salt 80% water 60% water 20% starch 40% starch 4. The diagram below describes a few different situations related to osmosis. Predict the end result of placing a red blood cell or Elodea plant cell into these situations. Draw what each cell type would look like after it has reached equilibrium. Cell will shrivel as water leaves cell through cell membrane. Elodea cell wall will remain the same. Cell will enlarge as water enters cell through cell membrane. Elodea cell wall will remain the same. Cell membrane may eventually burst. Cell will remain same size. It will be at equilibrium. 5. Would a cell lose or gain water when placed in a solution with a salt concentration greater than that of the cell cytoplasm? Cell will lose water. 6. Would a cell lose of gain water when placed in a solution with a salt concentration less that that of the cell cytoplasm? Cell will gain water. 7. Which way would the water molecules move in the following situations (in or out)? Then explain why the water molecules move in that direction. a. Cucumber slice is placed in salt water. Water will move out of the cucumber cells due to the fact that the water concentration is greater inside the cells than outside of the cells. b. Salt is poured onto a snail. Water will move out of the snail cells due to the fact that they contain more water than the outside environment. c. Vegetables are sprinkled with water Water will move into the vegetable cells because the vegetables contain less water than the surrounding environment. d. Potato slice is placed in pure water Water will move into the potato cells because they contain less water than the surrounding environment.