* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download midterm 16 review
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
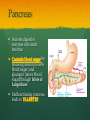
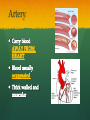
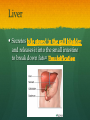
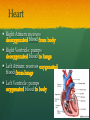
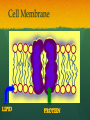
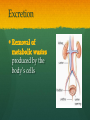
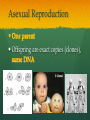
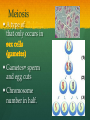
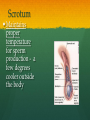
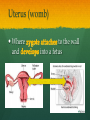
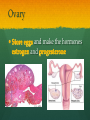
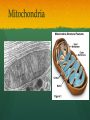
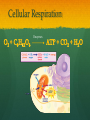
Nutrition Involves taking in nutrients = Ingestion Breaking them down = digestion And excreting waste = egestion Cellular Respiration Process by which glucose is broken down and energy is released in a all cells of Cellular Respiration gives off carbon dioxide CO2, ATP (energy), and WATER VAPOR It requires Autotroph Organisms that Heterotroph Must Pancreas Secretes digestive enzymes into small intestine by releasing insulin (lowers blood sugar) and glucagon (raises blood sugar)through Islets of Langerhans Malfunctioning pancreas leads to Hormones Special chemical messages sent to the body Shape specific Artery Cartilage tissue found between contact ( ) Osmosis Diffusion Movement of a substance from concentration This movement does not require energy= Passive Transport Liver Secretes and releases it into the small intestine to break down fats= Cell Membrane Double layer of molecules and and out of cell all in and Heart Right Atrium: receives blood Right Ventricle: pumps blood Left Atrium: receives blood Left Ventricle: pumps blood Homeostasis through small changes that keep the internal environment at a level needed for survival Cells The basic unit of structure and function in all living things (organisms) Bones System of levers that provides the body with , of internal organs, and means for Photosynthesis Water + Sunlight + Carbon dioxide + Chlorophyll Glucose + Oxygen Neurotransmitter Special chemical that between two neurons Cell Membrane Excretion produced by the body’s cells Platelets Small cell fragments that Carbohydrates and proteins are too big to pass through the cell membrane Must be broken down first into Carbohydrates Proteins Active Transport Movement across a membrane from an area of Requires extra cellular Receptors Cell membrane contains receptors which receive signals from other areas Receptor molecules are AIDS cquired mmune yndrome eficiency Caused by the HIV virus that gradually cells, weakening the immune system, and reducing the body’s ability to fight infections Histamine Substance the body releases that causes an , like sneezing etc. Negative Feedback 98.7° F A change (stimuli) causes a response in an attempt to Ex: Blood sugar is high, pancreas secretes insulin to lower blood sugar Ex: Body temperature too high– you sweat to cool body down Stomates/ Stoma Found on underside of leaves Special openings that allow to be Asexual Reproduction Offspring are exact copies (clones), Meiosis A type of that only occurs in Gametes= sperm and egg cuts Chromosome number in half. Scrotum Maintains proper temperature for sperm production - a few degrees cooler outside the body Uterus (womb) Where and to the wall into a fetus Ovary and make the hormones and Placenta Attached to the wall of uterus and fetus between mother Gametes Males: produced in testes Females: produced in ovaries Fertilization Fertilization= egg = fertilized Recombination= zygote contains genes from both parents that have recombined Differentiation – the zygote Copies itself by mitosis . Vaccine Injection of a small amount of a disease Allows body to Pulse (Heart) Rate The at which your Measured in beats per minute (bpm) Can be felt at arteries close to the skin’s surface (wrist, neck, upper arm) Changes in Pulse Rate Pulse rate changes based on the throughout the body to maintain homeostasis Normal pulse rate 60-90 bpm Meiosis See slide 31 for definition Cuts the chromosome number in half from 46 to 23 in sex cells Sperm cells (spermatogenesis): one sperm cell with 46 chromosomes becomes • Egg cells (Oogenesis): one egg cell divides into cell with and 3 nonfunctional egg cells Genetic Variation Meiosis is responsible for genetic variation - during meiosis, some segments of chromosomes are exchanged, creating genetic variation Genetic Recombination Zygote (fertilized egg) contains that have recombined Plant Cell Structures - extra layer located outside of cell membrane, provides rigid structure - green, contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis Photosynthesis Plants make their own food Glucose provides energy for all living organisms It must be converted into a useable energy form (ATP) through Mitochondria Site for - process by which glucose is broken down and energy is released in a Mitochondria Cellular Respiration Enzymes ATP Antigen Any substance in your body (bad thing) that causes This is known as the Antibody Defense mechanism body produces in Produced as part of the Proteins are made of amino acids Starches are made of simple sugars.