* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mr. Wilkinson`s APUSh Class
Survey
Document related concepts
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
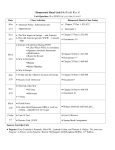
Pageant Ch. 36 HW: America in World War II, 1941-1945 Unified by Pearl Harbor, America effectively carried out a war mobilization effort that produced vast social and economic changes within American society. Following its “get Hitler first” strategy, the U.S. and its Allies invaded and liberated Europe from Nazi and Fascist rule. The slower strategy of “island-hopping” against Japan also proceeded successfully until the atomic bomb brought a sudden end to World War II. ALLIES: USA (FDR, Harry S Truman), United Kingdom (Winston S. Churchill), Soviet Union (Josepf Stalin), China (Chiang Kai-Shek), Free France (Charles de Gaulle) AXIS: Germany (Adolf Hitler), Japan (Hideki Tojo, Emperor Hirohito), Italy (Benito Mussolini) Objective 1: Explain how America mobilized for war against both Germany and Japan. 1. What was the ABC-1 Agreement? 2. Why was there “virtually no government witch-hunting of minority groups,” unlike WWI? 3. Describe the internment of Japanese-Americans. 4. What was the Supreme Court’s decision in Korematsu v. U.S.? 5. Briefly describe how the war effort revived the American economy (also refer to pp. 837-8). 6. Describe the efforts of the War Production Board. 7. Describe the efforts of the Office of Price Administration. 8. Why did labor unions resent the War Labor Board? 9. What was the Smith-Connally Anti-Strike Act? Objective 2: Describe the war’s effects on society, including regional migration, race relations, and women’s roles. 10. Which groups were the most notable of the “women in arms”? 11. Describe the bracero program. 12. What did “Rosie the Riveter” represent? 13. How did war industrialization affect migration and city growth patterns? 14. Who was A. Philip Randolph? Pageant Ch. 36 HW: America in World War II, 1941-1945 15. What did the “Double V” slogan call for? 16. How did war mobilization affect Native Americans? 17. Who were the “code talkers”? Objective 3: Explain the early Japanese successes in Asia and the Pacific and the American strategy for countering them. 18. After Pearl Harbor, what territories did Japan conquer? 19. Describe the Bataan Death March. 20. Who won and what was the significance of the Battle of the Coral Sea? 21. Who won and what was the significance of the Battle of Midway? 22. Who won and what was the significance of the Battle of Guadalcanal? 23. Explain the island-hopping (leapfrogging) strategy. 24. What was the significance of holding the Marianas? Objective 4: Explain the final military and diplomatic efforts that brught Allied victory in Europe. 25. Explain the significance of the Enigma codes. 26. What was the significance of the Battle of El Alamein? 27. What was the significance of the Battle of Stalingrad? 28. Why did the British prefer to attack Europe through the Mediterranean rather than France? 29. What did FDR and Churchill agree to at the Casablanca Conference? 30. Describe the results of the invasion of Sicily. Pageant Ch. 36 HW: America in World War II, 1941-1945 31. What did FDR, Churchill and Stalin agree to at the Teheran Conference? 32. Explain the invasion of Normandy on D-Day (June 6, 1944). 33. Why was Harry S Truman chosen to be FDR’s Vice Presidential candidate in 1944? 34. Describe the Battle of the Bulge. 35. Describe the Yalta Conference (check pg. 867). 36. Describe the discovery of the concentration camps. 37. Describe the final stages of the war in Europe. 38. What was V-E Day (May 7, 1945)? Objective 5: Explain the final military and diplomatic efforts that brought Allied victory in Asia and the significance of the atomic bomb. 39. Describe MacArthur’s return to the Philippines. 40. Describe the fire-bombing of Tokyo. 41. Describe the Battle of Okinawa. 42. Describe the kamikaze attacks. 43. What did Truman and Stalin agree to at the Potsdam Conference? 44. Why did Truman order the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki? 45. What was V-J Day (September 2, 1945)? 46. Why was “America alone untouched and healthy” after the war?