* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4 – Plate Tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
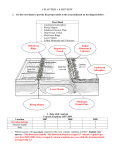
Chapter 4 – Plate Tectonics Study Guide Your success on the Plate Tectonics Summative Assessment depends upon your knowledge of: Earth’s Layers o Crust – Earth’s lightest material Oceanic is thinner and denser than continental crust o Mantle – makes up most of Earth’s mass o Lithosphere – crust and upper part of the mantle Rigid, outer-most layer Make up lithospheric plates o Asthenosphere –solid rock that flows lithospheric plates move on this part o Mesosphere –strong, lower part of the mantle o Outer Core – liquid o Inner Core – made mostly of iron Solid, dense center of the Earth Convection Currents o Occur in the asthenosphere o Hot material from deep in the Earth rises while cooler material near the surface sinks o Caused by heat and gravity Lithospheric Plates o Made of crust and upper part of the mantle o Thickest part lies beneath a mountain range o The thinnest part lies beneath the middle of the ocean Lithospheric Plate Boundaries o Convergent – plates push into each other Cause continental mountains o Divergent – plates move away, pull apart from each other Cause mid-ocean ridges o Transform-plated slide past each other o Slab pull Caused by heat and gravity Oceanic plate sinks and pulls the rest of the plate with it. o Ridge push Caused by heat and gravity Oceanic plate slides down o Has a Subduction zone Mountain Formation o Folded mountains –Earth’s crust being pushed up o Fault block mountains – sedimentary rock layers are tilted by faulting o Volcanic mountains magma reaches the Earth’s surface to form them Only type of mountain formed by adding new material to the Earth’s surface. Theory of Plate Tectonics o It is believed that fossils of the same land-living reptiles have been found in Antarctica, India and South Africa because these areas were once connected to each other. o Plate movement measured in centimeters per year You must answer the first question. Then choose ONE other question to answer. Explain how volcanoes form. Explain the difference between the crust and the lithosphere. List and describe three possible driving forces of lithospheric plate motion. When convection takes place in the mantle, why does cooler material sink, while warmer material rises? If the Earth's crust is growing at mid-ocean ridges, why doesn't the Earth itself grow larger? Give evidence that sea-floor spreading exists. You will be given diagrams of convergent boundaries. You will have to identify the types of plates that are colliding and which diagram creates the world’s tallest mountains.