* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Major Organic Groups - Lemon Bay High School
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
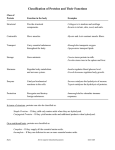
Major Organic Groups Monomer Monosaccharides Glucose Fructose Monomer Structure Carbohydrates Lipids No true monomer structures; very different for each class of lipids Polymer Polysaccharides Sucrose Starch Glycogen Phospholipids Steroids Proteins Dietary source Bread, cereals, potatoes, rice, simple sugars. Cell membrane structure Oils, nuts, butter, meats, eggs, dairy Membrane stabilizers, hormones Triglycerides Stored/circulating fats for energy Polypeptides or proteins. Largest variability in Meats, eggs, function but divided into dairy, nuts, soy 2 main categories Globular proteins are functional proteins (enzymes, hormones, antibodies, clotting factors) Fibrous proteins are structural proteins (muscle fibers, collagen, ligaments) These are fatty acid chains Amino acids 20 different amino acids that have same backbone (amine group and acid group) with different Rgroups Functions Fuel source for production of ATP. Cell surface receptors. Nucleic acids Nucleotides Made of nitrogen base, 5-carbon sugar [ribose or deoxyribose, and phosphate group(s)] DNA Store genetic info for protein synthesis RNA Use genetic info to construct and assemble proteins ADP/ATP Stored energy All living things that we eat that are most natural, little processed. Universal genetic code so we incorporate these nucleotides into our own genetic code when we make new cells.