* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORD
Survey
Document related concepts
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
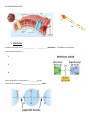
Applied Biology Chapter 2.3/2.4 Note sheet: Carbon Compounds/Enzymes Objectives: • Identify what makes an organic molecule “organic” • Identify/Recognize carbon skeletons & functional groups in organic molecules • Relate monomers to polymers • Describe the processes of building and breaking polymers (2 reactions involved) • Describe the basic structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids ORGANIC MOLECULES – _____________________-based molecules • Hydrocarbons – Organic molecules made of only ____________________ & ______________________ (example CH4) • Inorganic Molecules – Non-carbon based molecules – Examples: THE CHEMISTRY OF CARBON Carbon forms ___________________________________ with up to _______ other atoms, including other carbons as it tries to fill its outermost energy level. Carbon-based molecules have three general types of structures/ carbon skeletons: 1. 2. 3. CARBON SKELETONS: Label straight, branched or ring __________________ _______________ __________________ MACROMOLECULES – “Giant Molecules” Polymers vs Monomers • Many carbon-based molecules are made of many small subunits/pieces bonded together. _________________ – Small chemical unit that makes up a polymer - “one unit” ________________ – Molecules made up of many monomers “many units” – Process is known as ___________________________. Making and Breaking Polymers To Build a polymer a __________________________________ reaction is used . Each time a monomer is added to a chain a water molecule is released (Lose _______________) To Break apart a polymer, a _______________________________ reaction is used. Each time a monomer is broken from a chain a water molecule is added (Add _______________) There are four major macromolecules found in living things: 1. 2, 3, 4. 1. CARBOHYDRATES • • Carbohydrates are made of __________________________________________________________ (Ratio= 1Carbon: 2 Hydrogen: 1 Oxygen) • Are made up of monomers of simple __________________________ molecules. • The building blocks (simple sugar monomers) of carbohydrates are _____________________________. Monosaccharide – Disaccharide – Polysaccharides – Functions of Carbohydrates: 1. Provides ___________________ when they are broken down. (Hydrolysis Reaction) 2. Provides ______________ ________________ for living things. (Part of the cell structure) Types of Carbohydrates: Type of Carbohydrate Starch Cellulose Simple or Complex ________________ Complex Glycogen ________________ Glucose ________________ Function Stores extra energy _________________________________ Stores extra energy Supplies energy for cell activities 2. LIPIDS Lipids are _________________ molecules that include fats, oils, and cholesterol. Lipids are __________________________________________ molecules - “water fearing” Made up of many carbon chains called __________________ ________________. Fats and oils have different types of fatty acids.: Functions of Lipids: 1. Store ______________ when broken down 2. Waterproof coverings on cells 3. Make up cell membranes (_______________________________) PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER 3. PROTEINS Proteins are polymers of _____________ ___________ monomers (20 different ones exist) Parts of an Amino Acid : 1. 2. 3. Amino acids differ in side groups, or __________groups. Amino acids are linked by ________________________ bonds. Proteins and Levels of Organization 1. Primary Structure – is the ______________ of its amino acid. 2. Secondary Structure – is the ___________________ of the ____________________ chain. 3. Third Level Structure – is the _______________ - ___________________ arrangement of a chain. 4. Fourth Level Structure - is how the different chains are ______________ _____________ to each other. Functions of Proteins: 1. Control cell ____________________ 2. Control ______________ of reactions 3. Form important parts in ________________ 4. Move substances _____ and _______ of cells 5. Help to ______________ disease 4. NUCLEIC ACIDS Made up of monomers called ________________________. Nucleotides are made up of three parts: 1. 2. 3. Functions of Nucleic Acids: ______________ and ________________________ genetic information. CHEMICAL REACTIONS Chemical Reaction – A process that ___________________ one set of chemicals into another. Changes in _________________ occur in chemical reactions (Release or use energy) Chemical bonds are ___________________ and other bonds are __________________ during a chemical reaction ENZYMES • Many chemical reactions occur inside cells (Reactants products) • Enzymes are protein catalysts ________________________ the _____________________ a reaction. that ____________________________ reactions _____________________________________ needed by to • Activation Energy - The energy needed to ______________ __________ a reaction. • Catalyst – any compound that speeds up a reaction by _____________ the __________________ energy. • Enzymes are reaction specific! • Substrate – • Active site – • Enzymes always pick up another substrate when the active site is unoccupied!! They are never used up.