* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download One gene
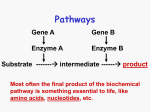
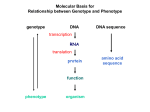
Survey
Document related concepts
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
One gene One enzyme hypothesis In the next few lectures, the following questions will be Addressed: 1 One gene One enzyme hypothesis In the next few lectures, the following questions will be Addressed: What is the structure of a gene? How does a gene function? How is information stored on the gene? What is the relationship between genotype and phenotype? 2 Pathways Biologists and clinicians want to address the question of how altering a particular set of base pairs that make up the 3 billion base pairs in the human genome led to this phenotype. 3 Alkaptonuria Degenerative disease. Darkening of connective tissue, arthritis Darkening of urine 1902 Garrod characterized the disorderusing Mendels rules- Autosomal recessive. Affected individuals had normal parents and normal offspring. 1908 Garrod termed the defect- inborn error of metabolism Homogentisic acid is secreted in urine of these patients. This is an aromatic compound and so Garrod suggested that it was an intermediate that was accumulating in mutant individuals and was caused by lack of enzyme that splits aromatic rings of amino acids. 1958 La Du showed that accumulation of homogentistic acid is due to absence of enzyme in liver extracts 1994 Seidman mapped gene to chromosome 3 in human 1996 Gene cloned and mutant identified P230S &V300G 2000 Enzyme principally expressed in liver and kidneys 4 How does a gene generate a phenotype? The experiments of Beadle and Tatum in the 1940’s provided the first insight into gene function. They developed the one gene/one enzyme hypothesis This hypothesis has three tenets: 5 Consequences of mutations Lets say we know the biochemical pathway. With this pathway, what are the consequences of a mutation in geneB? Would the final product be produced? Would intermediate2 be produced? Would intermediate1 be produced? What happens if we add intermediate1 to the media? What happens if we add intermediate2 to the media? 6 Neurospora Beadle and Tatum analyzed biosynthetic mutations in the haploid fungus Neurospora. It had the advantage in that it could be grown on a defined growth medium. 7 Arginine biosynthetic mutants Beadle and Tatum set out to identify genes involved in the biosynthetic pathway that led to the production of the amino acid arginine. Neurospora has approximately 15,000 genes and only 4-5 of these genes are involved in synthesizing arginine. How do you identify five genes from 15,000? The POWER OF GENETICS!!!!!! Typically the organism is exposed to a strong mutagen. This randomly mutagenizes genes. Then you look for a mutant in the pathway of interest. 8 The method complete 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 minimal 9 Conclusion-strain1 Strain1 and 7 are defective in either amino acid production or Vitamin production Complete media (salt+sugar+ Vitamin + amino acids) Minimal media Minimal media (salt+sugar) (salt+sugar) + 20 amino acids + vitamins Minimal media Complete media (salt+sugar) (salt+sugar) Vitamin + amino acid Conclusion: 10 Conclusion- strain7 Strain1 and 7 are defective in either amino acid production or Vitamin production Complete media (salt+sugar+ Vitamin + amino acids) Minimal media Minimal media Minimal media complete media (salt+sugar) (salt+sugar) (salt+sugar) (salt+sugar) + 20 amino acids + vitamins Vitamin + amino acids Conclusion: 11 Which amino acid? Beadle and Tatum found that three mutants could not produce arginine Arg1 Arg2 Arg3 The biochemical pathway for arginine synthesis was kind of known. Ornithine and citrulline are closely related to arginine and were thought to be precursors Instead of arginine, if they added ornithine or citrulline to the media, some mutants were rescued and others were not Precursor -----> ornithine -----> citrulline -----> arginine 12 Add back Precursor -----> ornithine -----> citrulline -----> arginine enz1 enz2 enz3 There are three different enzymes required for arginine synthesis Enz1, enz2 and enz3 Beadle and Tatum isolated three different mutations in genes (three genes) Arg1 Arg2 Arg3 ?????Which mutation codes for which enzyme???? Instead of arginine, if they added ornithine or citrulline to the media, some mutants were rescued and others were not Arginine Ornithine Citrulline Mutant1 Mutant2 Mutant3 13 Mutant in Arg1- only precursor made Add ornithine or citrulline to media, downstream enzymes are functional and pathway continues---> arginine synthesized Mutant in Arg2You need to supplement media with citrulline for the pathway to continue. Adding the precursor or ornithine does not help. Mutant in Arg3You need to supplement media with arginine. Adding the precursor, ornithine or citrulline does not help. These experiments demonstrated that a single gene (mutation) coded for a single enzyme. In addition, the combination of appropriate mutations and intermediates enabled Beadle and Tatum to define the biochemical pathway leading to Arginine synthesis. 14 This rationale currently is being used in many laboratories to elucidate more complex pathways in multicellular organisms キ Review Solving biochemical pathways: The more mutations that a compound rescues, the later in the pathway the compound is located Conversely, the later a mutation is in a pathway, the fewer 15 compounds will rescue it: Another example Mut1 Compound E B N A Mut2 Mut3 16 What is the order of the compounds and mutations in the pathway? The steps in a biochemical pathway identified by this procedure are dependent on the available intermediates and mutations. This procedure does not identify every step in the pathway 17 Biosynthetic pathways at the grocery store Most of the red and blue colors found in higher plants are a result of pigments synthesized from one of two metabolic pathways, the carotenoid or the anthocyanin pathway. Grocery store corn is usually yellow. Which step in the pathway must be mutated to produce yellow corn? 18 The Flavor-Saver Tomato Ethylene gas released by fruit accelerates the ripening process Prevention of ethylene production would block the fruit from ripening prematurely and spoiling on the way to the market. The ethylene biosynthetic pathway is as follows: Precursor-----> ACC------> ACC synthase ethylene ACC oxidase Which step in the pathway must be mutated to prevent Ethylene production? 19 Temperature-sensitive mutations The one gene/one enzyme concept explains a number of genetic phenomena A) Temperature-sensitive mutations Some mutations exhibit a phenotype at high temperatures (the restrictive temperature) but function normally at lower temperatures (permissive temperature). The mutation results in a slight destabilization and alteration of the 3D conformation of the enzyme An example of a TS mutation: Dogs and cats that are white with black feet or vice versa The gene for coat color is normal at cold temperatures The extremities are colder than the body, therefore the enzyme is active in the feet and produces color. Low temp- structure of enzyme- normal- activity normal High temp- structure of enzyme-altered- No activity These kinds of conditional mutants allow you to turn on and off a function of a protein. 20 Dominance versus Recessive The one gene/one enzyme concept explains a number of genetic phenomena B) Dominance versus Recessive Precursor------> product------> phenotype ^ | enzymeA ^ | geneA キ A allele produces functional enzyme キ a allele produces nonfunctional enzyme Genotype enzyme activity phenotype A/A 2X normal A/a 1X normal a/a 0X mutant Usually substrate is limiting, enzyme is in excess By saying that a mutation is recessive, we are saying that 1 unit (or 50% of the normal activity) is enough to produce a normal phenotype 21 Genetic Ratios The one gene/one enzyme concept explains a number of genetic phenomena C) Genetic Ratios The one gene/one enzyme hypothesis also explains phenotype ratios observed in a standard dihybrid cross: Precursor----> yellow intermediate----> white EnzA Parental cross product blue EnzB white x yellow 22 Precursor----> yellow intermediate----> white EnzA product blue EnzB F2 AB Ab aB ab AB Ab aB ab 9 A-B3A-bb 3aaB1aabb blue white yellow yellow 23 Labradors Parental Cross: black x yellow BBEE bbee BbEe (black) x BbEe (black) Yellow-------> E brown--------> black B Given the pathway show above, what phenotypic ratios would be produced in progeny from the dihybrid cross: BbEe x BbEe EB Eb eB eb EB 9:3:4 Eb eB eb 24 Precursor----> white intermediate----> white EnzA AB product blue EnzB Ab aB ab AB Ab aB ab 9 A-B3A-bb 3aaB1aabb blue white white white 25 Biochemical Pathways and Linked Genes Precursor----> yellow intermediate----> white EnzC GeneC Parental C-D C-D product blue EnzD GeneD x c-d c-d F1 The following F2 progeny are produced: 50 yellow 40 blue 10 white What is the map distance between these two genes? Map Distance+#Recombinants/Total Progeny x 100% 26 One gene: one polypeptide The concept of 1 gene/enzyme was modified to the concept of: 1 gene/ 1 protein Almost all enzymes are proteins but not all proteins are enzymes. Many proteins provide structural rather than enzymatic roles. For example polymers of the protein actin provide structural integrity to the eukaryotic cell. Perhaps the most notable example of this comes from studies of Hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron carrying protein found in the red blood cells and is responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the body. 27 Hb Hemoglobin consists of four polypeptides (proteins) each associated with a specific Heme group (Heme is a small iron containing molecule to which oxygen can attach) Adults contain 2 alpha polypeptides and 2 beta polypeptides Alpha polypeptide = 141 amino acids Beta polypeptide= 146 amino acids Over 300 known hemoglobin variants are known and each is the result of a specific mutation Most of these are the result of a single amino acid substitution キ Hb A: キ Hb S: キ Hb C: These results demonstrate that: 1. Genes specify proteins that are not enzymes 28 2. Mutations can disrupt a single amino acid out of the many that make up the protein.