* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MS Word
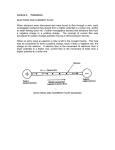
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
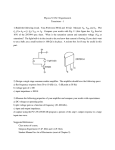
Name ______________________________ ES 330 Electronics II Homework # 4 (Fall 2016 – Due Monday, October 3, 2016) Problem 1 (25 points) An NMOS transistor is connected in the bias circuit shown below. It is biased at VG = 5 volts and RS = 3 k connected to ground. The transistor parameters are Vt = 1 volt and kn = 2 mA/V2. (a) What is the bias current ID (= IS)?. Page 1 (b) Now suppose we switch transistors where the new transistor has a 50% higher value for kn. By what percentage does drain current ID change as a result? Problem 2 (25 points) Consider the circuit shown below for an NMOS transistor having a Vt = 1 volt and with kn = 4 mA/V2. Let VDD = 5 volts and VSS = - 5 volts. Design for a DC bias drain current of 0.5 mA and for the largest possible voltage gain (that means for the largest value of RD) consistent with a 2-V peak-to-peak swing at the drain node. Simplifying assumption: Take the AC signal voltage on the source node to be essentially zero (i.e., meaning it remains at the DC terminal voltage you caluclated when determining VGS). Thus, the minimum drain node voltage vDrain will be 1 volt in magnitude in meeting the 2-V peak-to-peak output voltage swing requirement. Page 2 What is VGS? What values do you calculate for RD and RS? Problem 3 (25 points) The transistor used in the circuit shown below is to be biased at a collector current IC = 1 mA. Whereas the current gain of the transistor is “nominally” equal to 100, this type of BJT actually can range from = 50 (minimum) to = 150 (maximum). You are told that VCC = + 3 volts and RC = 2 k. (a) Find the required RB value to achieve IC = 1 mA for a “nominal transistor.” (b) What is the expected range of IC and VCE values from = 50 to = 150? Page 3 (c) Comment on the efficacy or viability of this design. Problem 4 (25 points) You are given a bipolar transistor amplifier which is drawn schematically below (See Figure 7.54 in Sedra/Smith): Using VCC = + 3 volts, design the circuit to have a collector current IC = 0.5 mA. The “nominal” of the transistor selected is 100. With = 100, find the value of resistor RC giving VCE = VCE(sat) + 1 volt = 0.3 V + 1 V = 1.3 V. (Note: An often assumed value for VCE(sat) is 0.3 V.) (a) Using “nominal” parameter values for the transistor, what is the base resistor RB value? Page 4 (b) If the resistor RB you pull out of the bin is low in value by 5% (remember resistors have tolerance ranges), how much does the emitter current IE change from what you calculated in part (a)?