* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell and Its Structures
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
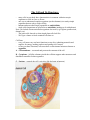
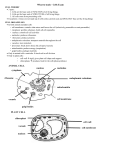
The Cell and Its Structures - many cells in your body have characteristics in common with microscopic organisms or cells in a tree or flower. - one way to understand complex organisms (such as humans) is to study simple organisms that are only a single cell big - humans and most other larger organisms are multicellular - single celled organisms are referred to as unicellular (nothing to do with phones) Note: you looked at some unicellular organisms last week (e.g. Euglena, paramecium, diatoms, etc) - The onion cells showed us what simple plant cells look like - We’ll get a chance to look at animal cells later on Cell Parts - every cell must carry out basic functions to stay alive (obtaining materials and supplies for energy, making products and getting rid of wastes) - to carry out these functions, cells must have certain internal structures known as organelles A – Cell membrane – surrounds and protects the contents of the cell B – Cytoplasm – jellylike substance inside the cell that supports other structures and distributes materials to other organelles C – Nucleus – controls the cell’s activities (like the brain in humans) D – Vacuoles – balloonlike spaces within the cytoplasm used for storage E – Cell Wall – occurs only in cells of plants and fungi – thicker and more rigid than cell membranes and are made of a tough material called cellulose F – Chloroplasts – structures within plants and some unicellular organism – responsible for photosynthesis PLANT CELL