* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Neurotransmitters
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
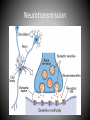
Neurotransmitters Ms. Carmelitano Introduction • Neurons are the building blocks of behavior – The 10 to 100 billion neurons make about 13 trillion connections with each other over the synapses • Essential Question: How do messages cross the synapses? Answer: Neurotransmission! • The neurons send electrochemical messages to the brain so that people can respond to stimuli • Neurotransmission: – The method by which messages are sent between the synapses of the neurons Neurotransmission • When an electrical impulse travels down the axon of the neuron, it releases neurotransmitters which cross the synapse between the neurons • Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers which transmit information over the synapses from one neuron to another. Neurotransmission • Neurotransmitters are stored in the neuron’s terminal buttons • When they cross the synapse they fit into receptor sites in the next neuron – like a lock-in a key, only certain neurotransmitters will fit in certain receptors • After the message is sent, other chemicals reabsorb the released chemicals Neurotransmission • Enough of the science… now for the effect on behavior! Effect on Behavior • Neurotransmission can cause many behavioral traits such as – Mood – Memory – Arousal – Mental illness Why? • Neurotransmitters are responsible for causing the body to react to stimuli • If the neurotransmitters are out of balance, they will not be able to cause the body to appropriately react to stimuli Effecting Neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters fit into receptor sites like a lock-and-key • Because of this, drugs can stimulate or block the neurotransmitter – This can be on purpose with prescription drugs to regulate over or under production or as a result of drug abuse Neurotransmitters you should know • • • • Acetylcholine Dopamine Norepinephrine Serotonin Activity • Using your textbooks and tablets, fill in the Neurotransmitters chart Acetylcholine • A neurotransmitter in the Autonomic Nervous System • In the PNS – helps with muscle contraction • In the CNS – sensory perception • Related to learning, memory, movement • If a person is having difficulty moving, it may be due to a blockage of acetylcholine Dopamine • • • • Helps with voluntary movement Learning Feelings of pleasure When we experience the stimuli of reward, there is an increase of the production of dopamine which creates the feeling of pleasure Norepinephrine • Can affect the rhythm of the heart • Helps to regulate flight-or-fight response • Stimulating affect, causing arousal, alertness, and stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system – Sympathetic nervous system – The system that aids in control of internal organs Serotonin • Regulates sleep, arousal, and emotion • Can regulate appetite • Can also affect memory and learning • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=90cj4NX8 7Yk • http://science.education.nih.gov/supplements /nih2/Addiction/activities/lesson2_neurotrans mission.htm