* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11/26 Aim: How did Rome go from Republic to Empire?
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman emperor wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
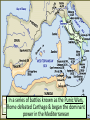
EQ: How did Rome go from Republic to Empire? Do Now: Analyze the following map of Rome in 44 BC. Answer the following Questions: 1. What inferences could you make about Rome by studying this map? 2. What might be some consequences of expanding your territory to this size? By the 3rd century B.C., the Romans conquered the Italian peninsula & began to exert power in the Mediterranean world But, the growth of Rome threatened Carthage, the superpower of the Mediterranean world In a series of battles known as the Punic Wars, Rome defeated Carthage & began the dominant power in the Mediterranean After the Punic Wars, Rome conquered new territories & gained great wealth One of the generals who led Rome’s expansion was a politician named Julius Caesar The Rise & Fall of Julius Caesar Julius Caesar took advantage of the chaos in Rome & was named dictator in 46 B.C. He initiated a series of reforms that offered Roman citizenship to conquered people & created new jobs Many Senators feared Caesar’s popularity & power as dictator of Rome In 44 B.C., Senators assassinated Julius Caesar The assassination led to another civil war led by Caesar’s adopted nephew Octavian & his best general, Marc Antony End of the Republic & Rise of the Empire ■Caesar’s death changed Rome: –People no longer trusted the Senate to rule Rome & the Roman Republic came to an end & the empire began The Roman Empire By 31 A.D, Octavian Augustus was name Rome’s first emperor; he served much like a King in that his power was absolute and he named his successors. This date marked the end of the Republic and the beginning of the Empire (imperial rule). The Roman Empire Augustus created a stable government which was centralized and bureaucratic and issued economic reform. For example, he made the tax system more fair. Augustus’ rule began a 200 year-span known as the Pax Romana (Roman Peace) - a period of peace and prosperity which ended after the death of Marcus Aurelius. The Roman Empire Social and Economic problems were hidden. To keep the restless mobs of people content, Roman emperors issued a policy of “bread and circus” in which the poor were given free food and all citizens were entertained using tax dollars. Close: Explain how Rome went from Republic to Empire.