* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Humans in the Biosphere (ch 6)
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Extinction debt wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Animal genetic resources for food and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Habitat destruction wikipedia , lookup
Holocene extinction wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
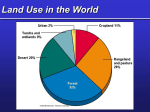
Humans in the Biosphere Chapter 6 Mrs. Yanac Limited Resources • All organisms on Earth must share the planet’s resources and they are LIMITED. • Humans are the main source of environmental change: o o o o Hunting & Gathering Agriculture Industry Urban development Hunting and Gathering • Prehistoric hunters and gathers changed the environment and even drove some species to extinction. Agriculture • Farming increased the amount of food produced & allowed cities to form • People in cities produced wastes • Advances in agriculture included use of pesticides & monoculture (planting of same crop year after year) which led to green revolution & an increase in world food supply • Problems Pollution from pesticides Industry • (-) Used more resources & produced more pollution than ever before • (+) Machines made life easier for humans Urban Development • Changes the landscape, displaces animals, destroys habitat, causes pollution, etc Renewable Resources • Any resource that can be easily replaced or replenished Nonrenewable Resources • Any resource that can NOT be easily replaced or replenished (takes millions of years to replace) Human Activities • Threaten many resources & can affect the quality & supply if renewable resources such as land, forests, fisheries, air & fresh water o Sustainable development is a way of using resources w/o depleting them • Soil erosion occurs when water or wind remove surface soil (removing nutrients & leaving land like a desert desertification) o Sustainable development would include alternating crop planting & contour planting Human Activities • Deforestation is the loss of forests which provide oxygen, wood, & other resources o Sustainable development would include planting trees to replace those cut down • Overfishing reduces fish populations o Sustainable development would include aquaculture (raising aquatic animals for food) Human Activities • Smog and acid rain are a result of air pollution due to burning fossil fuels o Sustainable development would include emission controls to reduce air pollution • Sewage & discarded chemicals can pollute the water supply o Sustainable development would include protecting wetlands & maintaining regulations on wastewater treatment Biodiversity • Biodiversity is the sum of all kinds of organisms in the biosphere • ECOSYSTEM DIVERSITY – all habitats, communities,& ecological processes in ecosystems • SPECIES DIVERSITY – the # of different species in the biosphere • GENETIC DIVERSITY – the genetic info carried in all living things on earth Ecosystem Diversity Species Diversity Genetic Diversity Threats to Biodiversity • Humans alter habitats, hunt species to extinction, introduce pollution into food webs & introduce foreign species into new environments • HABITAT FRAGMENTATION • EXTINCTION • BIOLOGICAL MAGNIFICATION • INVASIVE SPECIES Habitat Fragmentation Extinction • Several mass extinctions over geologic time (i.e. Dinosaurs) • Humans have driven many species to extinction On the verge of extinction • Many are listed as o THREATENED – Population numbers are rather low & they must be protected & monitored o ENDANGERED – Population numbers are extremely low and they must be protected, Conservation • Conservation is the wise management of natural resources • Protecting entire ecosystems as well as a single species • Protecting the ecosystem ensures that the natural habitat is preserved & the interactions of many different species at the same time. The Future • Effects on the Ozone Layer o Ozone protects Earth from harmful radiation o CFC’s (found in aerosols) caused damage to the ozone o CFC’s have since been banned • Global Warming o Increased production of CO2 has thickened the “blanket” around the earth resulting in the trapping of more heat, raising the average temperature of the planet o Runaway greenhouse effect (Global Warming) could result in coastal flooding and drastic weather patterns