* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download High concentration
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
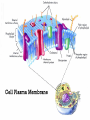
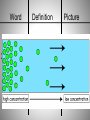
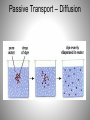
Diffusion and Osmosis Notes Objective: You will be able to explain diffusion and osmosis and give an example for each one. Itinerary: 1. PowerPoint (definitions) 2. Teacher demostrations The Plasma Membrane and Homeostasis Homeostasis – Maintaining a Balance • Cells must keep the proper concentration of nutrients and water and eliminate wastes. SO HOW DO THINGS GET INTO THE CELL? The cell doesn’t have a mouth, so particles have to go through the cell membrane! Word 1. Cell membrane Definition Surrounds cell Semipermeable: Lets certain things in and out of cell Picture Everything a cell needs to come in or go out has to pass through cell membrane Food molecules Carbon dioxide Oxygen molecules Wastes Water molecules The cell membrane has little spaces where things can just slip right in or out of the cell. So…. Some substances are so small that they can slip between the membrane molecules to enter or leave the cell. Imagine a jar full of marbles… Can you pour some sand into the jar? The sand will fill up the space in between the marbles…that’s how some materials can get through the cell membrane. What does passive mean? This lady is passive! Word 2. Passive Transport Definition No energy to move materials Examples: Diffusion and Osmosis Picture Word 3. Diffusion Definition When particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration HIGH TO LOW Picture Passive Transport – Diffusion Familiar examples of diffusion: • A skunk’s odor spreads through the neighborhood • A spilled bottle of perfume fills the air with a strong scent • Food coloring mixes through a beaker of water No energy is needed for oxygen to diffuse into a cell. • High concentration of oxygen outside of cell • Low concentration of oxygen inside the cell • Diffusion of oxygen into cell • Equal concentration of oxygen outside and inside cell No energy is needed for carbon dioxide to diffuse out of the cell. • High concentration of carbon dioxide inside of cell • Low concentration of carbon dioxide outside the cell • Diffusion of carbon dioxide out of cell • Equal concentration of carbon dioxide in and outside cell Word 4. Osmosis Definition Picture The diffusion of water across a membrane HIGH TO LOW LOTS OF WATER TO LESS WATER Osmosis – What is happening in this animation? What happened to the celery? Is this diffusion or osmosis? This celery is wilted, so we put it into water. Less water IN celery It is OSMOSIS! Water flowed into celery! Your blood is similar to sea water in the amount of salt it contains. What do you think would happen to one of your red blood cells if you placed it in pure water? Fresh water will flow into the cell and it will burst! Word 5. Equilibrium Definition when the molecules of a substance are spread out evenly throughout the Space - Osmosis and diffusion will continue until particles are equal Picture EXIT SLIP 1. Give definition and an example of diffusion (you may have seen some today in class) 2. Give a definition and an example of osmosis. 3. What is passive transport? 4. What is equilibrium?