* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes - Cell Processes
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
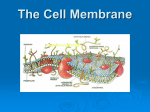
Cell Processes The Cell Membrane • The membrane that surrounds the cell and its organelles. – Acts as a gateways between the outside environment and a cell’s cytoplasm. – Selectively permeable – allow only certain substances in and out of the cell, not all substances. Solutions • Substances entering and leaving a cell, through the cell membrane, are dissolved in a liquid – solution. – Solutions are mixtures of two or more substances. • Substance that does the dissolving = solvent. – Water is the universal solvent. • Substance that is being dissolved = solute. Solvent = water Solute = sugar Solution Concentrations • The amount of substances being dissolved compared to the amount of substance doing the dissolving = concentration. – High concentration = high solute, little solvent • Ex. Very sweet lemonade = lots of mix (solute), little water (solvent) – Low concentrations = little solute, high solvent • Ex. Weak tasting lemonade = small amount of mix (solute), lots of water (solvent) Cell Transport • Substances are transported into or out of a cell in two ways: – Passive Transport – No energy is required to move the substances. – Active Transport – Energy IS required by the cell to move the substances. BrainPop – Active Transport Passive Transport • Cells move materials from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentrations – concentration gradient. • Depending on the substance being moved, transport occurs in two ways: – Diffusion = movement of particles – Osmosis = movement of water Diffusion • When particles in a solution are in constant motion, colliding, causing them to spread out. – continue to move until concentration is the same = Equilibrium. Examples: 1. Oxygen moving from your lungs to your bloodstream 2. Carbon dioxide moving from your bloodstream to your lungs 3. Nutrients moving from your small intestine into your bloodstream. Equilibrium Diffusion Through a Membrane • Process of Diffusion – animation Osmosis - Passive • The movement of water into or out of the cell from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration - Osmosis. – Perhaps the most important substance that passes through the cell membrane is WATER. – Cells can’t function properly without adequate amount of water. BrainPop – Passive Transport Osmosis Water is at equilibrium! Three solution types: Osmosis 1. Hypertonic Solution – higher water concentration inside the cell than outside a. Water will move out of the cell = shrink Three solution types: Osmosis 2. Hypotonic Solution – higher water concentration outside the cell than inside. a. Water will move into the cell = swell Three solution types: Osmosis 3. Isotonic Solution – equal concentrations of water inside and outside the cell. a. Water moves equally in and out of the cell. Osmosis in Blood Cells Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Active Transport • Some materials must be moved against the concentration gradient by active transport. – Energy IS required! • Two Methods: – Molecule Transport • The use of proteins in the membrane to move substances across the membrane. Cell Transport – Active Transport – Endocytosis and Exocytosis • Some cells take in or release materials through movements of the cell membrane using energy. Exocytosis