* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exocytosis and Endocytosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
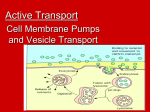
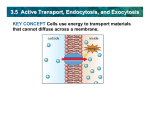
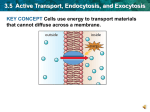
Exocytosis and Endocytosis Exocytosis and Endocytosis A Closer Look at Cell Membranes Aim: How do large particles enter and exit cells? Do Now: Name some molecules/materials that enter and exit the cell. How would you describe the cell membrane that allows passage of these materials? Exocytosis and Endocytosis Exocytosis and Endocytosis Exocytosis (out of the cell) • The fusion of a vesicle with the cell membrane, releasing its contents to the surroundings Endocytosis (into the cell) • The formation of a vesicle from cell membrane, enclosing materials near the cell surface and bringing them into the cell Exocytosis and Endocytosis Endocytosis Phagocytosis – solid Pinocytosis – liquid (general) Endocytosis: Uptake of substances Transport of protein or lipid components of compartments Metabolic or division signaling Defense to microorganisms Endocytosis Clathrin-coated vesicles Non-clathrin coated vesicles Macropinocytosis Potocytosis Exocytosis and Endocytosis Endocytosis Required: signal membrane receptor (Fc receptor for Ab) formation of pseudopodium cortical actin network The formed vesicle: phagosome (hetero-; auto-) Endocytosis Clathrin-coated vesicles Non-clathrin coated vesicles Macropinocytosis Potocytosis Endocytosis and Exocytosis Examples Three Pathways of Endocytosis Bulk-phase endocytosis • Extracellular fluid is captured in a vesicle and brought into the cell; the reverse of exocytosis Receptor-mediated endocytosis • Specific molecules bind to surface receptors, which are then enclosed in an endocytic vesicle Phagocytosis • Pseudopods engulf target particle and merge as a vesicle, which fuses with a lysosome in the cell Phagocytosis (“engulfment”) Exocytosis and Endocytosis Membrane Cycling Exocytosis and endocytosis continually replace and withdraw patches of the plasma membrane New membrane proteins and lipids are made in the ER, modified in Golgi bodies, and form vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane Exocytic Vesicle 5.5 Key Concepts: Membrane Trafficking Large packets of substances and engulfed cells move across the plasma membrane by processes of endocytosis and exocytosis Membrane lipids and proteins move to and from the plasma membrane during these processes Exocytosis and Endocytosis Macropinocytosis Ruffling of the surface membrane forms inclusions These „vacuoles” have no membrane Size 0.2-5 mm - the mass/surface ratio is very good Significance: Liquide-phase pinocytosis Taking probes from the environment – antigene recognition in macrophages Exocytosis and Endocytosis Exocytosis in TEM THE END