* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Léčiva působící prostř. histaminu, serotoninu a dopaminu
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of TRPV1 antagonists wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
CCR5 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Atypical antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Norepinephrine wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
Chlorpromazine wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
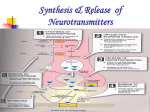
Drugs acting by inhibition or activation of receptors for dopamine, serotonine and histamine Practice pharmacology, medical students III.yr. November 2013 Dopamine and dopamine receptors Effect of antagonists of dopamine A/ Antipsychotic effect 1/ Typical antipsychotics (1. generation): chlorpromazin, haloperidol 2/ Atypical antipsychotic agents (2. generation): a/ clozapin, olanzapin, risperidon, ziprasidon, quetiapine b/ sulpirid and amisulpirid: D2, D3 antagonists 3/ Dopaminergic „stabilisator“ = presynaptic agonist/postsynaptic antagonist of D2 receptor and 5-HT2 antagonist aripiprazol B/ Antiemetic effect metoclopramid, domperidon, itoprid Drugs used in the treatment of Parkinson´s disease 1. Agonists of dopamine receptors: bromokriptin /D2/, ropinirol, pramipexol, rotigotine 2. Inhib. of MAO-B: selegilin, cannot be combined with L-DOPA 3. COMT inhibitors: entacapon 4. L-DOPA SEROTONIN, (5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMIN, 5-HT) • Serotonine receptors: 5HT1A, 5-HT2, 5-HT3, 5-HT „xyz“ Clinical effects of activation/inhibition of serotonine receptors 5HT-1A agonist = anxiolytic and antidepressant eff. 5-HT2 antagonist eff. = antipsychotic eff., improvement of sleep • 5-HT3 antagonists: antiemetic effects ondansetron, granisetron, tropisetron etc. • 5-HT1A agonist: buspiron - anxiolytic drug, approved indication GAD, can be used also as add-on for alcoholics, with care as add-on to some antidepressant medication • 5-HT1D (1B) agonists: antimigrenic effects sumatriptan, naratriptan, zolmitriptan etc. Antidepressants blocking serotonine receptors • 5-HT2 • Agomelatine = agonist at melatonine receptors and antagonist at 5-HT2 rcp. (should not be combined with alcohol, regular control of AST and ALT is necessary) • 5-HT-2 and 5-HT-3 • Mirtazapine = noradrenergic and specific serotoninergic antidepressant HISTAMINE and histamine receptors • Histamine receptors H1, H2 and H3 • Antagonists of H1 receptors alleviate symptoms of alergic reactions, can have antiemetic, sedative effects • 1/ Sedative – promethazin, hydroxyzin (hydroxyzine is biotransformed to cetirizine), bisulepine etc. • 2/ Not sedative – cetirizine and levocetirizine, loratadine and desloratadine • 3/ Not sedative antihistaminic drug blocking effect of PAF /platelet activ. factor/ = rupatadin /rupatadine is metabolised to desloratadine/ Histamine and histamine receptors • Antagonists of H2 receptors - ranitidine, famotidine, (historical example cimetidine) • Antagonists of H3 receptors = betahistin for Meniere disease and problems like tinnitus, hearing loss Questions 2/ What antihistamine drugs can be considered as immunomodulatory (= can have antiinflammatory effect) and why? levocetirizine, desloratadine 1/ Treatment with and rupatadine: clinically these drugs will have antagonists of histamine H1 receptor also some effect on nasal obstruction is symptomatic or (levocetirizine inhibits migration of eosinophils to causal therapy of the site of allergic reaction, desloratadine inhibits allergic diseases? expression of adhesion molecules or inflammatory cytokines, rupatadine blocks also effect of PAF in It is symptomatic addition to ihibitory effects on histamine release) treatment. 3/ What are possible combinations of antihistaminic drugs with other drugs for treatment of allergy in clinical practice? E.g.: cetirizine+mometasone (local corticosteroid); desloratadine+montelukast (both p.o.)