* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Expansion of the Universe
Anthropic principle wikipedia , lookup
History of gamma-ray burst research wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
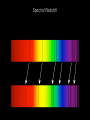
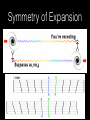
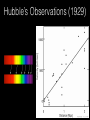
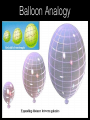
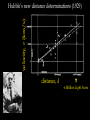
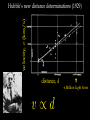
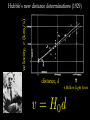
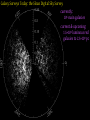
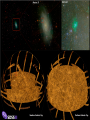
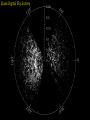
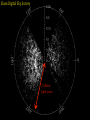
How we know the Universe is expanding Physics 20B Prof. Kevork Abazajian - filling in for Prof. Virginia Trimble - Doppler Effect Cosmological Redshift Origin of Redshift Spectral Redshift Cosmological Redshift There are four phenomena that cause light to be seen as "redder" than the source that actually emitted it. 1. Scattering of blue and green light - i.e. why the sky appears blue, and why some sunrises or sunsets may appear red. Dust, smoke from forest fires, or other intervening material between the source and the observer can scatter (remove) the higher frequency colors (blue, green, yellow, and orange) leaving mainly the red colors. However, this effect does *not* cause a frequency shift of the light waves. A spectrum of the source will not have any of its atomic lines displaced. 2. Gravitational Redshift - where the photons incur a loss of energy overcoming the effects of a gravity well. Since the energy of a photon is directly proportional to its wavelength, a high energy photon will suffer a wavelength increase as it looses energy in this manner. Also note that this is a "one-time" event - once the photon has escaped the source's gravity well, its wavelength is constant again. 3. Doppler Redshift - is caused by the relative motions of a source and an observer. Doppler redshifts may be towards the red (source moving away from the observer) or towards the blue (source moving towards the observer). Doppler redshift is an effect of the relative motions of nearby objects and does NOT involve the expansion of the Universe. 4. Cosmological Redshift or "Hubble redshift" - is caused by the relativistic expansion of the Universe, as quantified by the Hubble constant, h0, and since the expansion rate increases with distance, the redshifts of very distant objects can be extremely large. As a result, the wavelengths of photons propagating through the expanding Universe are stretched by the expansion of space itself, creating the cosmological redshift. Origin of Redshift Symmetry of Expansion Symmetry of Expansion Hubble’s Observations (1929) Hubble Expansion Observations (1996) Another way to look at data Expansion of all of space… Everything moves away from everything else Expansion of all of space… Everything moves away from everything else Balloon Analogy Expansion of all of space… raisin bread analogy! Expansion of all of space… raisin bread analogy! What is the Universe expanding into? This question is based on the ever popular misconception that the Universe is some curved object embedded in a higher dimensional space, and that the Universe is expanding into this space. This misconception is probably fostered by the balloon analogy which shows a 2-D spherical model of the Universe expanding in a 3-D space. While it is possible to think of the Universe this way, it is not necessary, and there is nothing whatsoever that we have measured or can measure that will show us anything about the larger space. Everything that we measure is within the Universe, and we see no edge or boundary or center of expansion. Thus the Universe is not expanding into anything that we can see, and this is not a profitable thing to think about. Just as Dali's Corpus Hypercubicus is just a 2-D picture of a 3-D object that represents the surface of a 4-D cube, remember that the balloon analogy is just a 2-D picture of a 3-D situation that is supposed to help you think about a curved 3-D space, but it does not mean that there is really a 4-D space that the Universe is expanding into. For objects in our ordinary experience, like the rising loaf of raisin bread dough also used as an analogy to the expanding Universe, there are two ways to see that the object is expanding: 1. The distances between objects are all increasing, so the distance between any pair of raisins increases by an amount proportional to the distance. 2. The edge of the loaf pushes out into previously unoccupied space. Note the distance between any pair of points on the edge increases by an amount proportional to the distance. The first statement involves the internal geometry of the object, which can be measured by an observer sitting in the object. The second statement involves the external geometry of the object, which can only be measured by an observer outside the object. Since we are stuck within our spacetime, we need to study the internal geometry of space-time, and that is what general relativity does. In terms of internal geometry, any object with the first property above is expanding. Furthermore the Universe is homogeneous so it does not have any edge. Thus it can't have the second property above. But it does have the first property so we say the Universe is expanding. The Universe in 1785: Herschel’s Map Star map assuming constant luminosity and density The Universe in 1785: Herschel’s Map Star map assuming constant luminosity and density The Sun The Universe in 1921: The Shapley Model velocity, v (km/s) Hubble’s new distance determinations (1929) distance, d 6 Million Light Years velocity, v (km/s) Hubble’s new distance determinations (1929) distance, d v/d 6 Million Light Years velocity, v (km/s) Hubble’s new distance determinations (1929) distance, d 6 Million Light Years v = H0 d Galaxy Surveys in 1985 CfA: 1100 galaxies in 6˚ × 130˚, in this slice Galaxy Surveys Today: the Sloan Digital Sky Survey currently: 106 main galaxies current & upcoming: 1.5×106 luminous red galaxies to 2.5×109 pc Sloan Digital Sky Survey: Galaxies from Large to Small Scales Sloan Digital Sky Survey: Galaxies from Large to Small Scales SDSS-III Spectrograph: 1000 Objects at a Time SDSS-III Spectrograph: 1000 Objects at a Time – 1000 fibers feed light from the focal plane into the spectrographs SDSS-III Spectrograph: 1000 Objects at a Time – 1000 fibers feed light from the focal plane into the spectrographs – Hand plugged SDSS-III Spectrograph: 1000 Objects at a Time – 1000 fibers feed light from the focal plane into the spectrographs – Hand plugged The Largest Color Image of the Sky Ever Made SDSS Sky Coverage & Scale Credits: D. Hogg, M. Blanton, D. Finkbeiner, D. Schlegel, N. Wherry Our local universe: the Laniakea Supercluster of Galaxies (Tully et al 2014) Sloan Digital Sky Survey Sloan Digital Sky Survey 2 billion light years SDSS Fly through: https://youtu.be/uGe475zySrM Quiz Three possible sources of energy might be suggested for the Sun and stars. How long would the Sun live if A. its energy source was chemical, like the burning of gasoline B. its energy source was gravitational, gradually released as it contracted from a cloud of gas and dust C. its energy source was nuclear, the fusing of hydrogen to helium Extra credit: what kinds of evidence or data or observations have suggested each of those time scales