* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecstasy
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic noise wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
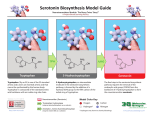
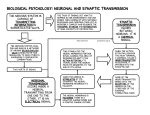
How Ecstasy Works DIRECTIONS: 1. DRAW each step on a different paper. 2. LABEL the underlined parts for each step. 3. USE titles to introduce the drug and related neurotransmitter(s) and for transitions between normal function and when taking the drug. 4. NARRATE each drawing in Photo Story by reading the appropriate step. Practice saying the terms first!! Normal Function of the Neurotransmitter Serotonin… 1. Vesicles in the sending neuron are filled with the neurotransmitter called serotonin. Dopamine plays an important role in mood regulation, appetite and your senses. 2. There are 10 serotonin receptors on the receiving neuron that receive the serotonin signal. 3. There are 5 recycling receptors on the synapse of the sending neuron that pick the serotonin back up after it does its job. 4. Serotonin is released from the vesicles into the synaptic gap. 5. Serotonin travels across the synaptic gap and fits with the serotonin receptors on the receiving neuron. This passes the signal along and results in the sensation of pleasure. 6. Serotonin disconnects from the serotonin receptors and is recycled into the sending neuron through the recycling receptors. 7. Vesicles reform. The person takes Ecstasy… 8. Ecstasy enters the synaptic gap. 9. Ecstasy is taken up by the recycling receptors. 10. The recycling receptors are confused by the ecstasy and start working backwards by pumping extra serotonin into the synaptic gap. 11. Serotonin builds up in the synaptic gap because it cannot be taken back up by the recycling receptors. This over-stimulates the receiving cell.