* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Galectin
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
5-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
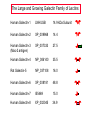
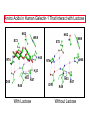
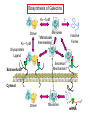
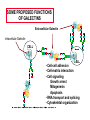
ESSENTIALS OF GLYCOBIOLOGY LECTURE 21 MAY 7, 2002 Richard D. Cummings, Ph.D. University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center College of Medicine Oklahoma Center for Medical Glycobiology “THE S-TYPE LECTINS (GALECTINS)” The Large and Growing Galectin Family of Lectins Human Galectin-1 LNHUGB 14.9 kDa Subunit Human Galectin-2 XP_009968 14.4 Human Galectin-3 (Mac-2 antigen) XP_007333 27.5 Human Galectin-4 NP_006140 35.5 Rat Galectin-5 NP_037108 16.0 Human Galectin-6 XP_008181 48.8 Human Galectin-7 I55469 15.0 Human Galectin-8 XP_002045 34.9 The Large and Growing Galectin Family of Lectins Human Galectin-9 XP_006105 XP_006104 35.5 (short form) 39.1 (long form) Human Galectin-10 XP_009208 15.6 Rat Galectin-11 AAC71765 15.8 (GRIFIN-(Galectin-Related Inter-fiber protein) Human Galectin-12 AAG40863 AAG40864 AF314686 34.6 (splice variant) 34.5 (splice variant) Human Galectin-13 NP_037400 15.3 Sheep Galectin-14 Human Urate Transporter/Channel 17.0 U67958 36.3 Distribution of Galectins Type Galectin-1 Galectin-4 Source h,r,m, ha;b,p h,m h,r,m, d,ha h,r,p,m Galectin-5 r Galectin-6 Galectin-7 Galectin-8 Galectin-9 m h,r h,r h,r,m Galectin-10 h Galectin-11 r Galectin-2 Galectin-3 Distribution most tissues Remarks Most common and abundant galectin small intestine Minor rel. to Gal-1 macrophage, N-terminal domain colon, most tiss. is collagen-like alimentary tract Linkage of two CRDs is protease-sensitive erythrocytes 85% identical to Cterm. CRD of Gal-9 gastrointestinal 85% ident. to Gal-4 skin marker of stratified epithelia liver, kidney,lung thymus, kidney C-terminal domain 85% Hodgkin’s lymp. identical to Gal-5 eosinophil, Charcot-Leyden basophil crystal protein lens (Grifin) may represent a new lens crystallin,galectinrelated inter-fiber protein H-human;m-mouse;m-monkey;r-rat; b-bovine;p-porcine;d-dog;ha-hamster Conserved Carbohydrate-Recognition Domain of Galectins F P C M L F G L S V — H— —N— —R—X —V— R—N— —X —W— E —X— E —X C T 4 A M Q 5-10 K V H N I I L N D L L Q P E I I E R C N V G — K —X — — V —G —X— —X — — — H 3 K M 3-6 T M S E F H F F K S C V Human Galectin-1 69-WGTEQREAV--FPFQPGSVAEVCITFDQANLT---VKLPDGYEFKFPNRL-WGTEQRETV--FPFQKGAPIEITFSINPSDLT---VHLP-GHQFSFPNRL70 Chick-14K Galectin phylogenetic tree of galectin family members percentages of protein identities among CRDs of human galectin family members Crystal Structure (1.7 Å) of Dimeric Human Galectin-1 Crystal Structure (1.7 Å) of Dimeric Human Galectin-1 With Bound Lactose Sideview Turned 90˚ Amino Acids in Human Galectin-1 That Interact with Lactose N62 N62 W69 E72 W69 E72 H45 R74 H45 R74 H2O H53 D55 H53 N47 R49 With Lactose D55 N47 R49 Without Lactose Biosynthesis of Galectins Kd ~7mM Dimer Kd ~1mM Glycoprotein Ligand ? Monomer “Metastable Intermediate” Inactive Forms * Secretion Mechanism? Extracellular Cytosol N Dimer Monomer 5’ mRNA 3’ SOME PROPOSED FUNCTIONS OF GALECTINS Extracellular Galectin Intracellular Galectin CELL CELL • Cell-cell adhesion • Cell-matrix interaction • Cell signaling Growth arrest Mitogenesis Apoptosis • RNA transport and splicing • Cytoskeletal organization Old Galectin Dogma New Info about Galectins Require reducing conditions for activity Can retain activity without reducing conditions in presence of ligands Occur only as soluble proteins Spliced forms may generate membrane-anchored proteins Bind terminal Gal Bind GalNAc, Gal, at internal and terminal positions, and sialylated Gal(NAc) Not post-translationally modified, other than Nterminal acetylation Some galectins may be phosphorylated, glutathionylated, cross-linked by transglutaminase Are galectins always dispersed in the cytosol and localized in the nucleus? Galectin-1 is localized to myofibrils of porcine cardiac cells Acetone Fixed Frozen Section Background Staining: 2 Ab only (H/E Stained) 1 mAb to Galectin-1 + 2 Ab (H/E Stained) Background on Galectin-1 Galectin-1 originally isolated from electric organ of electric eel (called electrolectin) (Teichberg et al, 1975). Subsequently identified in mammalian heart and lung (de Waard and Kornfeld, 1976) and embryonic chick muscle (Nowak and Barondes, 1976). Galectin-1 binds laminin, a basement glycoprotein(Zhou and Cummings, 1990) lamp glycoproteins (Do, Smith & Cummings, 1990); fibronectin (Ozeki, et al, 1995); and a7b1 integrin (Gu et al, 1994); ganglioside (Kopitz et al, 1998); and CD45 (Perillo et al, 1995). Galectin-1 (and others) secreted by non-classical pathway (Hughes, 1994; Cho and Cummings, 1995). Background on Galectin-1 Galectin-1 is mitogenic for lymphocytes (Pitts and Yang, 1981), but has a growth-inhibitory activity for some mammalian cells (Wells & Mallucci, 1991) which is apparently independent of their beta-galactoside binding site (Scott & Zhang, 2002). Galectin-1 is able to induce apoptosis in some types of cells (certain T-cell subsets) (Rappl et al, 2002) Background on Galectin-1 Galectin-1 activates the neutrophil respiratory burst and may have proinflammatory functions (Almkvist et al, 2002); activates Ca2+ intracellular rise (Walzel et al, 1996). Galectin-1 in drosophila is expressed in a developmentally-regulated tissue- and cell specific manner (Pace et al, 2002) Background on Galectin-3 Galectin-3 originally identified as macrophage antigen Mac-2;and occurs both on the cell surface and intracellularly. Upon apoptotic stimulation, galectin 3 becomes enriched in the mitochondria and prevents mitochondrial damage and cytochrome c release (Yu et al, 2002) Galectin-3 contains the NWGR motif shared by bcl-2 family members; gal3 binds bcl-2 in a lactoseinhibitable manner (Yang et al, 1996; Akahani et al, 1997) Background on Galectin-3 Galectin-3 suppresses apoptosis (anti-apoptotic) and anoikis; such suppression may contribute to cell survival during metastatic cascades; this suppression requires phosphorylation of Ser6 (Yoshii et al, 2002) Galectin-3 proposed to play a role in b2-integrinindependent neutrophil extravasation (Sato et al, 2002) During involution of the mammary gland galectin-3 expression is up-regulated and occurs in non-apoptotic cells (Mengwasser et al, 2002) Background on Galectin-3 An alternatively spliced form of chicken galectin-3 contains a predicted transmembrane spanning domain and leucine zipper motif (Gorski et al, 2002) Galectin-3 ligands include Lamp glycoproteins, IgE, laminin, intestinal mucins, and Mac2 binding protein and cytokeratin (Goletz et al, 1997). Background on Galectins-7,-8,and -9 Galectin-7 (also called PIG1) intracellularly expressed exhibits pro-apoptotic function through JNK activation and mitochondrial cytochrome c release (Kuwabara et al, 2002) Galectin-8 expression is inversely related to tumour growth rate (Nagy et al, 2002) Galectin-9 (also known as ecalectin) represents a novel class of eosinophil chemoattractants (ECAs) produced by activated T cells (Sato et al, 2002; Matsumoto et al, 2002) Further Background on Galectins Intracellularly, galectins may exist in a glutathionylated form (Fratelli et al, 2002) Galectin-14 expressed in eosinophils and its release may contribute to eosinophil function and allergic inflammation (Dunphy et al, 2002) Galectins-1, -3, and -14 contain a Bcl-2-like motif; through this motif these galectins may regulate apoptosis (38-41). In particular, it has been postulated that Bcl-2 and galectin-3 may heterodimerize through this motif to inhibit Fas-antibodymediated apoptosis (Yang et al, 1996; Akahani et al, 1997; Perillo et al, 1997). Further Background on Galectins Many galectins have already been linked to immunity (Vasta, et al, 1999). Galectins regulate cytokine production (Cortegano et al, 19989; Vespa et al, 1999), stimulate thymocyte apoptosis (Galectin-1; Chung et al,2000; Pace et al 2000; Galectin9 - Wada et al, 1997), activate respiratory bursts of neutrophils and mast cells (Yamaoka et al, 1995); and migration of leukocytes (Matsushita et al, 2000; Sano, et al, 2000). Galectins 1, 3, 10, 11 and 14 appear to localize simultaneously to the nucleus and cytoplasm under various conditions (Dunphy, et al, 2000). Further Background on Galectins The role galectins play in the nucleus remains unclear, but it has been postulated that galectins 1 and 3 regulate pre-mRNA splicing (Dagher et al, 1995; Vyakarnam et al, 1998; Dunphy et al, 2000). The specific presence of galectin-14 in eosinophils and its release during inflammatory reactions into the lung fluid indicate that the protein may play an important role in allergic-type responses, in particular in allergic asthma (Dunphy et al, 2002). Unexpectedly, the C-terminus of the human urate transporter/channel contains the galectin CRD (related to galectin-5) in a transmembrane protein (Leal-Pinto et al, 1997). Information about Galectin Function from Mouse Genetics Galectin 3(-/-) mice develop fewer inflammatory cell infiltrations in the peritoneal cavities than the wild-type (gal3(+/+)) mice in response to inflammatory stimuli, mainly due to lower numbers of macrophages (m). Also, when compared to cells from gal3(+/+) mice, thioglycollate-elicited inflammatory cells from gal3(-/-) mice exhibited significantly lower levels of NF-kappaB response. Information about Galectin Function from Mouse Genetics Different cell-spreading phenotypes are observed in cultured (m) from the two genotypes; (m) from gal3(+/+) mice exhibited well spread out morphology, those from gal3(-/-) mice were often spindle-shaped. Peritoneal (m) from gal3(-/-) mice are more prone to undergo apoptosis than those from gal3(+/+) mice when treated with apoptotic stimuli (Hsu et al, 2000). Information about Galectin Function from Mouse Genetics Galectin 1(-/-) mice have generally normal phenotypes and litter sizes (). Galectin 1(-/-) mice have disrupted axonal architecture for a subset of olfactory neurons (Puche et al, 1996); this is supported by in vitro work which showed that galectin-1 promotes binding between olfactory neurons and a laminin glycoconjugate that lines the axonal migration path in vivo (Mahanthappa et al, 1994). In vitro galectin-1 can induce programmed cell death in T-cells in a CD45-dependent manner (Perillo et al, 1995).