* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Core concepts - WordPress.com
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
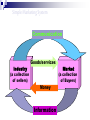
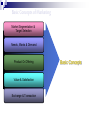
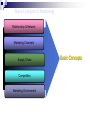
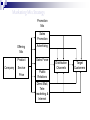
What is Marketing? Marketing is societal process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering and freely exchanging products and services of value with others. What is Marketing Management? Marketing management is the art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping, and growing customers through creating, delivering, and communicating superior customer value. Simple Marketing System Communication Industry Goods/services (a collection of sellers) Market (a collection of Buyers) Money Information What is Marketed? Ideas Goods Events Organizations Place Information Services Scope Persons Experiences Properties Basic Concepts of Marketing Market Segmentation & Target Selection Needs, Wants & Demand Product Or Offering Value & Satisfaction Exchange & Transaction Basic Concepts Market The set of actual and potential buyers of a product. These people share a need or want that can be satisfied through exchange relationships. Segmentation and Targeting Market Segmentation: Divide the market into segments of customers Target Marketing: Select the segment to cultivate Segment 1 Segment 2 Need, Want and Demand Needs - State of felt deprivation including physical, social, and individual needs. Wants - Form that a human need takes, as shaped by culture and individual personality. Demand – Want along with buying power converts into demand. Marketers and Prospects Marketer: Someone seeking something to another party. Prospect: Someone seeking something from another party. to sell to buy Value & Satisfaction Value = Benefit Cost Benefit = Functional Benefit + Emotional Benefit Cost = Monetary Cost + Time Cost +Energy Cost + Psychic Cost Satisfaction Customer Satisfaction: Dependent on the product’s perceived performance relative to a buyer’s expectations. If performance (P) is lower If performance (P) is higher than expectations (E), than expectations (E), satisfaction is low. satisfaction is high. E=10 > P=8 E=10 < P=12 Exchange & Transaction Exchange: Obtaining a desired product from someone by offering some thing in return. Five conditions must be satisfied: •At least two parties •Each should have something of value to the other party •Each party is capable of communication and delivery •Each party is free to accept or reject the exchange offer •Each party believes it is desirable to deal. Transaction: It is a trade of values between two or more parties. •Monetary Transaction: Money is paid against goods •Barter Transaction: Trading goods or services for other goods or services. Basic Concepts of Marketing Relationship & Network Marketing Channels Supply Chain Competition Marketing Environment Basic Concepts Relationship & Network Relationship marketing has the aim of building long term mutually satisfying relations with key parties: •Customers •Suppliers •Distributors •Stake holders •Employees Outcome Marketing Network Marketing Channels Communication Channels • Dialogue Channels • Distribution Channels Channels Physical Distribution Channels • Monologue Channels Service Distribution Channels • Selling Channels •Distributor & Retailers •Insurance Co. •Banks Supply Chain Competition 1 Brand Competition Other companies offering a similar product and services to the same customers at similar prices. 2 3 4 Industry Competition Form Competition Generic Competition All companies manufacturing products that supply the same service. All companies that compete for the same consumer money. All companies making the same product or class of products (all price range) Marketing Environment Internal Environment Micro Environment Macro Environment Marketing Mix Marketing Mix is the set of marketing tools that the firm uses to pursue its marketing objective. Four P’s and Four C’s Product: Customer Solution Price: Customer Cost Place: Convenience Promotion: Communication Marketing Mix Product Product Variety Quality Design Features Brand Name Packaging Sizes Services Warranties Returns Price List Price Discounts Allowances Payment Period Credit Terms Promotion Sales Promotion Advertising Sales Force Public Relations Direct Marketing Place Channels Coverage Assortment Locations Inventory Transport Marketing Mix Strategy Promotion Mix Sales Promotion Company Offering Mix Advertising Product Sales Force Service Price Public Relations Direct Mail, Telemarketing & Internet Distribution Channels Target Customers Summary Marketing Management is creating, communicating superior customer value. delivering, It has a wider scope. Marketing starts with recognition of needs of customer. and Then segmentation and selection of market is done to choose a specific kind of need to fulfill. Then product is positioned in the minds of the customer. Marketing has four important P’s: Product, Price, Promotion and Place. Product is placed in the competitive environment. Customer is satisfied when the product meets his expectation. Company’s focus is to earn profit through customer satisfaction.