* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Principles of Marketing (Mkt571)
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
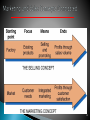
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Topic One: Marketing: Creating & Capturing Customer Value 1 Understand the marketing concept as a management philosophy (or ‘The way we do things in our organisation’). Recognise the central importance of an external focus looking towards building a viable organisation by satisfying customers’ needs and wants in a competitively sustainable way. Compare and contrast common managerial philosophies: production orientation, product orientation, selling orientation, financial orientation, social orientation, marketing orientation, and societal marketing orientation. Reflect upon the evolutionary development of contemporary marketing thought and practice 2 How many of this class have consumed something today How many of you have purchased something today How many have seen or heard an advertisement How many of you have engaged in word-ofmouth advertising about products or services… often without realising this has happened? 3 Marketing has been going on for centuries, it is a fundamental practice of humans: ◦ It is part of daily life ◦ It happens all over the world ◦ We can learn to make better consumer decisions from studying marketing Marketing can have a positive impact on a countries economy ◦ Overall marketing is approximately 50% of retails expenses ◦ Healthy marketing systems support economic advances 4 Marketing management is essential to long term organisational success! Build a better mousetrap? And the world will beat a path to your door, or does it??? ◦ 80-90% of new products fail ◦ Same rate for new businesses They need managing! Marketing is all about people (consumers) and it is fun ………(Well I thing more fun than maths and physics!) 5 Marketing communications are not always honest and they can sometimes play on emotions and fears. They can also cause harm by people buying things they do not need. Youth can be targeted by companies selling adult products (like alcohol) Some advertisements are crude Advertising can be annoying especially telemarketers, spam and informercials Advertising can be boring Fashion advertising can promote unobtainable body types. 6 Can push people to buy things they do not need Sometimes tells us that buying things makes us happy Sometimes can take advantage of consumer lack of knowledge (let the buyer beware) 7 Usually tries to be successful by satisfying customer needs and desires Often delivers the customers what they want, when they want it, at a price they are willing to pay. 8 A management philosophy based on the idea that, in a competitive environment, the odds of achieving strong organisational performance will be improved by having… “an absolute dedication to understanding and satisfying the needs of customers in well-defined target markets.” (Kotler et al 2003 p.4) The goal of Marketing is to facilitate exchange i.e. the transfer of products, services or ideas with a return form of payment. 9 Simple Definition: Marketing is managing profitable customer relationships. Goals: 1. Attract new customers by promising superior value. 2. Keep and grow current customers by delivering satisfaction. 10 Marketing needs a marketplace….a market. A market is a collection of buyers and sellers of a particular product, service, idea Marketing needs a medium of exchange e.g. money, goods in kind, time in lieu etc To be really successful marketing needs management and coordination 11 The set of actual and potential buyers of a product. These people share a need or want that can be satisfied through exchange relationships. 12 A private individual or household with needs and wants to satisfy. In other words a buyer just like you or your family. Marketers often use the term ‘B2C’ to express the idea of a Business marketing to Consumers. 13 An organisation (such as a business) with needs and wants to satisfy. Note: the terms customer and consumer are often used interchangeably Marketers often use the term B2B to express the idea of a Business marketing to another Business 14 Market demand is based upon central needs that provide the motivation to acquire products and services. Needs can be fundamental and physical and also individual. 15 Needs - state of felt deprivation including physical, social, and individual needs. 16 17 Wants are needs translated into a product or service offering that is appropriate to the consumer e.g. a microwave meal, an NMIT business course, a music CD, and new car etc 18 Wants - form that a human need takes, as shaped by culture and individual personality. 19 Needs and Wants Fulfilled through a Marketing Offer : ◦ Some combination of products, services, information, or experiences offered to a market to satisfy a need or want. 20 Products Anything that can be Offered to a Market to Satisfy a Need or Want Persons Places Information Organizations Ideas Services Activity or Benefit Offered for Sale That is Essentially Intangible and Does Not Result in the Ownership of Anything 21 Market demand reflects the fact that just because someone WANTS a product it does not necessarily follow that there is an actual opportunity to obtain it. Demand can exist only if that person can afford to buy it (available funds) and has access to the product (it is in stock, legal to own) 22 Wants Buying Power “Demand” 23 Sellers pay more attention to the specific products they offer than to the benefits and experiences produced by the products. They focus on the “wants” and lose sight of the “needs.” 24 When a consumer interacts with a marketing firm, an exchange relationship exists. The consumer aims to get a product that satisfies a NEED and WANT to go away happy and satisfied The firm wants to sell this product and to go away happy and satisfied that it has made a profit on the transaction or exchange. 25 Marketing is all about two parties exchanging value (the consumer gives up money to get satisfaction; the firm gives up a product to get a profit). There is no ‘residual discontent’ – the consumer does not feel cheated and ripped off and the firm is not in despair that it has not made a profit on the transaction. 26 Marketing is not about achieving one-shot deals and transaction. It is about building long-term, value-for-value RELATIONSHIPS with good customers. A loyal customer is a stream of future earnings for the marketing business and who is going to refer the business to friends, family and associates. “Marketing is about selling products that don’t come back to customers that do!” 27 Societal Marketing Concept Marketing Concept Selling Concept Product Concept Production Concept 28 29 30 31 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. The Marketing Concept (completed) Company and Marketing Strategy Analysing the Marketing Environment Managing Marketing Information Customer Driven Strategy Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning Products, Services & Brands Pricing policy Placement policy Advertising & Public Relations Sale Promotion & Personal Selling Consumer & Business Buyer Behaviour Direct & Digital Marketing Ethics & Marketing Compliance 32 #1 #2 Market Segmentation: Divide the market into segments of customers Target Marketing: Select the segment to cultivate 33 Dependent on the product’s perceived performance relative to a buyer’s expectations. 34 Expectation 8 Performance 10 Expectation Performance 10 8 If performance is lower than expectations, satisfaction is low. If performance is higher than expectations, satisfaction is high. 35 Customer’s evaluation of the difference between all the benefits and all the costs of a marketing offer relative to those of competing offers. 36 Basic Relationship Continuum Full Partnership 37 Social Benefits Financial Benefits Structural Ties 38 The process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction. 39 Customer Lifetime Value ◦ The entire stream of purchases that the customer would make over a lifetime of patronage. Share of Customer ◦ The share a company gets of the customers purchasing in their product categories. 40 Target Markets and Segmentation Needs, Wants, and Demands Product or Offering Value and Satisfaction Exchange and Transactions Relationships and Networks Marketing Channels Supply Chain Competition Marketing Environment 41