* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CP Physics Semester 1 Final Exam Review Packet 2016
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
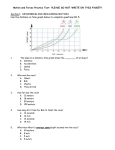
Name___________________________________________________________ Period____ CP Physics Semester 1 Final Exam Review Packet 2016 1. List the six steps of the scientific method. 2. What is a variable in the scientific method? 3. What is an independent variable? 4. What is a dependent variable? 5. What is a control variable? 6. Which axis is the independent variable graphed on? 7. Which axis is the dependent variable graphed on? 8. What are the three things that must be on a proper graph? 9. What is the equation for any straight line and what does each letter represent? 10. What is the equation to find the slope of a line? 11. If a line runs through points (3,5) and (9, 17), what is the slope? Acceleration vs. Mass Mass (kg) Acceleration (m/s2) 1 2.5 2 4 3 5.5 4 7 5 8.5 12. Graph the data above on the graph to the right. A C C E L E R A T I O N (m/s2) 13. What is the slope of the above graph? Mass (kg) 14. What are the units of the slope? 15. What is the value of the y-intercept? 16. What is the unit for the y-intercept? 17. What are the three trig functions and what are their ratios? 18. What is sin (53o) equivalent to? 19. Draw a right triangle. The hypotenuse is 23 meters long and one other side is 15 meters. Find the remaining side, and all three angles. 2 20. Solve the following triangles for all sides and angles. 3 m 5 meters 410 5 meters 21. What is the correct algebraic order of operations? 22. Solve 130 = 12𝑀 for M. 23. Solve 92 = 950 𝐺 for G. 24. In scientific notation, the decimal always goes after the first ________number. 25. What is the definition of accuracy? 26. What is the definition of precision? 27. What are the metric prefixes you need to know, including their values in reference to the base unit. 28. Convert 25 mm to cm. 29. Convert 340 cm to m. 3 30. Convert 0.5 meters to cm. 31. Convert 1.2 km to m. 32. Convert 94 km to cm. 33. What is the definition of distance? 34. What is the definition of displacement? 35. A person walks 30 meters east, followed by 25 meters north. They do this in 45 seconds. a. What is the distance travelled? b. What is the displacement (include direction). c. What is their average speed? d. What is their average velocity? 36. What is the SI unit for distance? 37. What is the SI unit for time? 38. What is a scalar quantity? 39. What is a vector quantity? 4 40. Give two examples of scalar quantities. 41. Give two examples of vector quantities. 42. What unit of distance should you use if you are measuring the length of a chalk? 43. What unit of distance should you use if you are measure the length of a flight? 44. If a car travels 200 meters in 23 seconds, what is the average speed? 45. If a boat has to travel 30 miles and it travels at 4 miles per hour. How long will the trip take? 46. A race car travels at 93 m/s for 21 seconds, what distance does it cover? 47. What is the definition of acceleration? 48. What is the acceleration due to gravity on Earth? 49. List the motion equations. 50. A car accelerates from rest at 4.5 m/s2 for 3 seconds. a. What is the car’s velocity after 3 seconds? b. What distance does the car travel in the 3 seconds? 51. A snowboarder is on the top of a 44 meters long incline. Starting from rest, they reach a velocity of 22 m/s at the end of the 44 meters incline. a. What is the snowboarder’s acceleration? b. How long does it take for the snowboarder to reach the ground? 5 52. A bungee jumper stands 200 meters up in the air on a ledge. They accidentally drop a penny. Ignore air resistance. a. What is the acceleration of the penny? b. How long will it take for the penny to reach the ground? c. How fast will the penny be travelling when it reaches the ground? 53. What is the definition of inertia? 54. What is the definition of a force? 55. What is Newton’s First Law of Motion? 56. What is Newton’s Second Law of Motion? 57. What is Newton’s Third Law of Motion? 58. What are the five main types of forces and explain where you would see each one? 59. What is another term for force of gravity? 60. How are weight and the force of gravity different? 6 61. What is the SI unit for weight? 62. What are the two types of friction? 63. What does the coefficient of friction tell us? 64. How do you calculate the coefficient of friction? 65. What is the weight of a 12 kg object on Earth? 66. Draw a force diagram (free-body diagram) for a block hanging from a string. 67. Draw a force diagram for a car travelling at highway speed at CONSTANT velocity. 68. Draw a force diagram of a student sitting at rest in a desk. 69. Draw a force diagram of a block on a ramp at rest. 70. What is the acceleration due to gravity? 7 71. A car (mass = 1100 kg) is pushed with a 4500 N force. a. What is the acceleration? b. What is the distance covered in 5 seconds? c. What is the velocity after 5 seconds? 72. What is the mass of a bus that accelerates at 3.1 m/s2 from a 1700 N force? 73. What is the definition of work? 74. What are the main three mechanical energies? 75. What is the equation for gravitational potential energy? 76. What is the equation for kinetic energy? 77. What is the equation for elastic potential energy? 78. What is the equation for work? power? 79. What it the unit for work? energy? power? 80. If a person (mass = 45 kg) is standing on a hill 20 meters in the air, what is their gravitational potential energy? 81. If a person (mass = 45 kg) is travelling at 9 m/s on the ground, what is their kinetic energy? 82. What is the energy of a spring (k = 400 N/m) that is stretched 0.24 meters? 8 83. If a person (mass = 45 kg) is rollerblading at 9 m/s on a 20 meters tall ledge, what is their total energy? 84. If an object (mass = 2.1 kg) is sitting on the ground, and it is lifted up to a shelf 2.6 meters tall, how much work was done? 85. How much power does a crane have that lifts a 400 kg box up 24 meters in a time of 30 seconds? 86. Define the conservation of energy. 87. If a ball is sitting on the top of a ramp, 5 meters off the ground, how fast will it be travelling when it rolls down onto the ground? 88. What is the definition of momentum? 89. What is the unit for momentum? 90. What are the two types of collisions? 91. Describe conservation of momentum. 92. What equations are used to solve for momentum problems? 93. What variables will have an impact on an object’s momentum? 94. What is an example of an elastic collision? 95. What is an example of an inelastic collision? 96. A 325 kg motorcycle is moving at 20 m/s south. Find its momentum. 9 97. Initially a soccer ball is going 23.5 m/s, south. In the end, it is traveling at 3.8 m/s, south. The ball's change in momentum is 17.24 kg m/s, north. Find the ball's mass. 98. A 62.0 kg curler travelling at + 1.72 m/s runs into a 78.1 kg curler and the 62.0 kg curler comes to a stop. If the 78.1 kg curler was originally moving at + 0.85 m/s, find his velocity after the interaction. 10 Fill out chart below: Term vector/ scalar Symbol(s) SI Unit Definition x 2 position distance speed displacement velocity weight mass acceleration force coefficient of friction 11 Term vector/ scalar Symbol(s) SI Unit Definition x 2 work kinetic energy gravitational potential energy elastic potential energy power spring constant momentum impulse time 12