* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download safety
Survey
Document related concepts
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
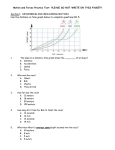
SAFETY _______1. a) b) c) d) Gently waving the fumes from a container toward one’s face, allows us to: safely test the odor of those fumes. test the sharpness of a scalpel. heat a substance and smell it at the same time. test if a substance is a strong acid. _______2. When dealing with heat or fire: a) hot plates should be on when not in use. b) heat liquids quickly. c) point container being heated away from partner but at the teacher. d) use tongs or “hot hands” to handle hot materials _______3. If you were to accidentally break some glassware in the classroom you should: a) ignore it and pretend nothing happened b) clean it up and then tell the teacher c) have a student clean it up while you tell the teacher d) tell the teacher and have her dispose of it properly _______4. When dressing for the laboratory, you should: a) wear loose fitting clothing. c) wear open-toed shoes. b) tie back long hair. d) all of the above. _______5. When heating a substance in a test tube, the opening of the test tube should a) be closed off to prevent any materials from exiting the test tube. b) point down toward the tabletop. c) point toward the teacher. d) point away from you and others. MEASUREMENT _______6. How many centimeters are in 5.75 meters? a) 575 c) 57.5 b) 5750 d) 0.575 _______7. The second is to time as the meter is to: a) kilometer c) density b) length d) mass _______8. Which of the following terms describes the amount of space an object occupies? a) temperature c) volume b) density d) mass _______9. Which of the following describes the amount of matter that something is made of? a) kilometer b) length c) density d) mass SCIENTIFIC METHOD ______10. The statement “Penicillin has no effect on bacteria, based upon the results of several experiments” is an example of a(n) a) observation c) problem b) conclusion d) hypothesis ______11. In which step do you develop an experiment to address your hypothesis? a) data & observations c) conclusion b) hypothesis d) procedure ______12. For a hypothesis to be scientifically useful, it must be: a) testable b) original c) written d) complicated ______13. Which one of the statements below accurately characterizes an observation? a) serves to explain data taken in by any or all of the human senses b) must involve the use of at least one of the human senses c) categorizes objects and/or events according to similarities d) serves as an explanation for an inference ______14. In which step do you ask a question about something you have observed? a) problem c) conclusion b) data & observations d) hypothesis ______15. Which step would you put a graph under? a) data & observations c) conclusion b) hypothesis d) procedure ______16. During the night, Steve was awakened by a thunderstorm. Walking to school the next day, he saw a tree blocking the street. The best inference he could make is that the tree was: a) hit by a bulldozer c) knocked down by the storm b) bombed by an airplane d) destroyed by a fire ______17. Scientists must analyze the results of an experiment before they form a (an) a) hypothesis c) control b) experiment d) conclusion ______18. A predicted answer to a problem is known as a(n) a) scientific law b) theory c) hypothesis d) scientific method ______19. You are conducting an experiment in which you are testing the effects of water temperature on the rate at which Kool-Aid dissolves. The variable in this experiment is: a) Kool-Aid c) water b) salt d) water temperature MOTION & SPEED _______20. A change in direction would change: a) acceleration b) speed c) velocity d) both a and c ______21. Which of the following factors determine velocity? a) speed c) acceleration b) direction d) both a and b ______22. A horizontal line on a distance vs. time graph shows that the object’s speed was a) increasing c) zero b) decreasing d) impossible to tell ______23. The acceleration that occurs in circular motion is known as: a) rapid acceleration c) kinetic acceleration b) centripetal acceleration d) circular velocity ______24. A car is traveling at a speed of 30 m/s. What time will it take to travel 90 m? a) 3 seconds c) 0.33 seconds b) 3 minutes d) 0.33 minutes ______25. A roller coaster is traveling at a speed of 3 meters per sec. What distance will it have traveled in 9 seconds? a) 3 meters c) 3 seconds b) 0.33 meters d) 27 meters ______26. Objects are accelerating when they are: a) increasing speed c) changing direction b) decreasing speed d) all of the above ______27. Speed is described in measurements of a) distance b) distance and time c) time d) mass and time ______28. Which of the following is a measure of velocity? a) 70 kilometers per hour c) 70 kilometers per hour due east b) northwest and 70 kilometers per hour d) both b and c ______29. A frog hops 2 meters in 4 seconds. At what speed did the frog travel? a) 0.5 s/m c) 2 s/m b) 0.5 m/s d) 2 m/s ______30. A woman standing on the ground watches an airplane fly by a mountain on a clear summer day. Her reference point for the moving plane would be a) The Great Wall of China c) the mountain b) the ground d) both a) and c) ANSWER QUESTIONS 31-34 USING THE FOLLOWING GRAPH MOTION OF A CAR 125 Distance (m) 100 75 50 25 0 1 2 3 4 5 Time (min) ______31. What distance has the car traveled at 2 minutes? a) 25 meters c) 50 meters b) 75 meters d) 100 meters ______32. How long did it take the car to go 100 meters? a) 2 minutes c) 4 minutes b) 3 minutes d) 5 minutes ______33. What is the speed of the car at 5 minutes? a) 0.04 m/min c) 25 min/m b) 0.04 min/m d) 25 m/min ______34. What is the speed of the car at 0.5 minutes? a) 0.04 m/min c) 25 min/m b) 0.04 min/m d) 25 m/min FORCES ______35. An object accelerates as it falls to the ground because: a) no friction is present. c) no force is acting on it. b) the object is lighter than air. d) gravity is pulling on the object. ______36. The amount of force acting on a moving object can be measured by determining the object’s mass and: a) inertia. c) acceleration. b) gravity. d) momentum. ______37. A miniature rocket with a mass of 4 kg must accelerate at 8 m/s2 in order to clear the building. How much force must the rocket exert? a) 2 N c) 0.5 N b) 32 N d) 12 N ______38. Which of the following statements is FALSE? a) Motion with a constant velocity is an example of balanced forces. b) Moving objects do not slow down on their own. c) Moving objects continue their motion until forces change. d) Balanced forces cause changes in motion. ______39. Friction acts: a) in a direction opposite to the motion of an object. b) to increase the speed of a moving object. c) to decrease the mass of a moving object. d) in the same direction as a moving object. ______40. A fish swims at an acceleration of 1.5 m/s2 and exerts a force of 30 N. What is its mass? a) 20 kg c) 0.05 kg b) 2 kg d) 0.5 kg ______41. A force is a) a push that affects matter b) a pull that affects matter c) a push or pull that affects matter d) none of the above ______42. Seat belts protect you from the effects of a) Newton’s third law of motion c) Newton’s first law of motion b) Newton’s second law of motion d) all of the above ______43. Which of Newton’s Laws of motion has to do with rockets being able to maneuver in outerspace: a) Newton’s 1st Law c) Newton’s 3rd Law nd b) Newton’s 2 Law d) Rockets can’t maneuver in a vacuum ______44. Which of the following would NOT occur due to gravity? a) A tennis ball and a bowling ball fall at the same speed when dropped off a building. b) The moon orbits around the earth. c) A person parachuting speeds towards the earth after jumping from an airplane. d) All of the above occur due to gravity. ______45. A feather and a rock dropped at the same time from the same height would land at the same time when dropped by a) Galileo in Italy c) an astronaut on the moon b) Newton in England d) an astronaut on the space shuttle ______46. Which one of the following is NOT a type of friction? a) sliding b) moving c) static d) fluid ______47. A rocket’s movement through space is determined by: a) nuclear forces between stars c) atmospheric pressures in space b) the direction of the gases it releases d) electric forces of the stars. ______48. A soccer ball with a mass of 2 kg is kicked with a force of 70 N. What is the acceleration of the soccer ball? a) 0.029 m/s2 c) 140 m/s2 b) 14 m/s2 d) 35 m/s2 ______49. Newton’s third law of motion deals with forces acting on: a) one object. c) objects of the same mass. b) different objects. d) objects of the same weight. DENSITY & BUOYANCY ______50. Which of the following forces helps boats float? a) electromagnetic force c) gravitational force b) nuclear force d) buoyant force ______51. An object weighs 50 N. It displaces a volume of water that weighs 45 N. What is the buoyant force on the object. a) 45 N b) 5 N c) 50 N d) 1.11 N ______52. If you pour a mystery blue fluid (density 2.3 g/mL) into a pitcher of water (density 1.0 g/mL), what will happen? a) water will sink to the bottom c) blue fluid will rise to the top b) blue fluid will sink to the bottom d) impossible to tell ______53. If the buoyant force on an object is greater than the object’s weight, the object will a) sink. c) rise to the surface and float. b) hover beneath the surface of the water. d) be crushed by the water pressure. ______54. If an object with a density of 30 g/cm3 is cut into two equal pieces, what is the density of each piece? a) 60 g/cm3 b) 30 g/cm3 c) 15 g/cm3 d) 1 g/cm3 ______55. An object that is completely underwater displaces a volume of fluid that a) is less than its own volume c) is equal to its own volume b) is more dense than itself d) is greater than its own volume ______56. Which is NOT an example of buoyancy? a) floating on your back in a pool b) a duck on the water c) drinking from a water fountain d) a fish in the ocean