* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning Target
Survey
Document related concepts
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
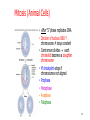
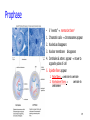
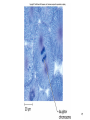
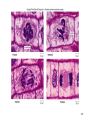
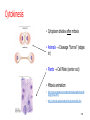
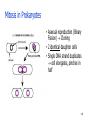
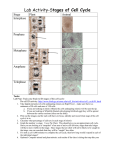
Learning Target 6. Recognize the type of daughter cells formed through mitosis and their chromosome number as compared to the parent cell. 1-1 Chromosome Number • Each species has unique chromosome # no relationship to complexity • Diploid--2n 2 copies of each chromosome (1/Mom & 1/Dad) (Homologous pairs) • All somatic cells (body cells) are 2n • Haploid--1n 1 copy of each chromosome (either Mom’s or Dad’s) • Only gametes (sperm/eggs) are 1n 1-2 Mitosis (Animal Cells) • After “S” phase replicates DNA • Division of nucleus ONLY ! chromosome # stays constant • Centromere divides each chromatid becomes a daughter chromosome • M checkpoint-stops if chromosomes not aligned • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase 1-3 Prophase • 5 “events” memorize them! 1. Chromatin coils chromosomes appear 2. Nucleolus disappears 3. Nuclear membrane disappears 4. Centrioles & asters appear move to opposite poles of cell 5. Spindle fibers appear 1. Polar fibers centriole to centriole 2. Kinetochore fibers centriole to centromere 1-4 1-5 Metaphase • Kinetochore fibers push chromosomes to middle of cell 1-6 1-7 Anaphase • Kinetochore fibers separate break centromeres pull chromatids to opposite poles of cell • Characteristic “V” shape 1-8 1-9 Telophase • Reverse of Prophase 1-10 1-11 Mitosis—Plant Cells • Mitosis in plant cells • Same phases as animal cells • Plants don’t have centrioles or asters 1-12 1-13 Cytokinesis • Cytoplasm divides after mitosis • Animals Cleavage “furrow” (edges in) • Plants Cell Plate (center out) • Mitosis animation: • http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/anisamples/majorsbi ology/mitosis.html • http://vcell.ndsu.edu/animations/mitosis/movie-flash.htm 1-14 Image found 11/29/4 on https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcT5zNgamn0R-M0Lufaxzvr5aXdjNYL1fb7lelcyz6w4Wwc7PEsTFQ 1-15 Mitosis in Prokaryotes • Asexual reproduction (Binary Fission) Cloning • 2 identical daughter cells • Single DNA strand duplicates cell elongates, pinches in half 1-16 Benefits of Mitosis • Genetically identical daughter cells • Take advantage of good conditions rapidly • Algal blooms 1-17