* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Histology
Survey
Document related concepts
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Nerve guidance conduit wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
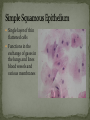
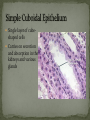
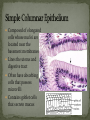
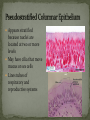
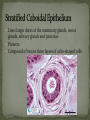
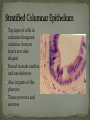
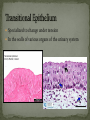
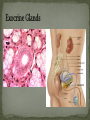
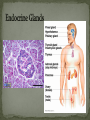
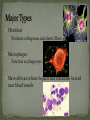
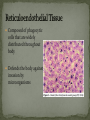
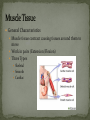
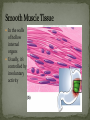
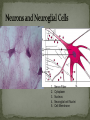
Histology The Study of Tissues Chapter 5 Cells are arranged in tissues that perform specialized structural and functional roles Four Major Types of Tissue: Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous General Characteristics Covers free body surfaces Major tissue of glands Anchored to connective tissue by basement membrane Lacks blood vessels Contains little intercellular material Replaced continuously Functions to protect, secrete, absorb and excrete Single layer of thin flattened cells Functions in the exchange of gases in the lungs and lines blood vessels and various membranes Single layer of cube- shaped cells Carries on secretion and absorption in the kidneys and various glands Composed of elongated cells whose nuclei are located near the basement membranes Lines the uterus and digestive tract Often have absorbing cells that possess microvilli Contains goblet cells that secrete mucus Appears stratified because nuclei are located at two or more levels May have cilia that move mucus or sex cells Lines tubes of respiratory and reproductive systems Composed of many layers Protects underlying cells Covers the skin Lines the mouth, throat, vagina and anal canal Lines larger ducts of the mammary glands, sweat glands, salivary glands and pancreas Protects Composed of two or three layers of cube-shaped cells Top layer of cells in contains elongated columns, bottom layers are cubeshaped Found in male urethra and vas deferens Also in parts of the pharynx Tissue protects and secretes Specialized to change under tension In the walls of various organs of the urinary system Composed of cells specialized to secrete substances Glands consist of one or more cells Exocrine glands secrete into ducts Endocrine glands secrete into tissues fluid or blood Exocrine glands classified according to the composition of their secretions Merocrine glands secrete fluid without loss of cytoplasm Apocrine glands lose portions of cells during secretion Holocrine glands release cells filled with secretory products Serous cells secrete watery fluid with high enzyme content; mucous cells secrete mucus. General Characteristics Connects, supports, protects, provides framework, fills spaces, stores fat, produces blood cells, protects against infection, helps repair damaged tissues. Located some distance apart Intercellular matrix consists of fibers and ground substances Fibroblast Produces collagenous and elastic fibers Macrophages: Function as phagocytes Mast cells can release heparin and histamine located near blood vessels Collagenous fibers Composed of collagen and have great tensile strength Dense Connective Tissue Tissue consisting mainly of collagenous fibers Elastic Fibers Composed of microfibrils embedded in elastin and are elastic Reticular Fibers Very fine collagenous fibers Dense Connective Tissue Reticular Fibers Forms thin membranes between organs Found beneath skin and between muscles Specialized form of loose connective tissue that stores fat Found beneath skin, certain abdominal membranes, around kidneys, heart, and joints Composed of strong collagenous fibers Found in tendons, ligaments, white portions of the eyes and deep layer of skin Provides framework Composed of fibers and gel-like ground substance Usually enclosed in a perichondrium Lacks direct blood supply and is slow to heal Major Types Hyaline Elastic fibrocartilage Contains mineral salts and collagen Cells usually in concentric circles around osteonic canals and are interconnected by canaliculi Active tissue that heals rapidly Transports substances and helps maintain a stable internal environment Composed of red cells, white cells, and platelets suspended in plasma Formed by special tissue in the hallow parts of certain bones Composed of phagocytic cells that are widely distributed throughout body Defends the body against invasion by microorganisms General Characteristics Muscle tissue contract causing tissues around them to move Work in pairs (Extension/Flexion) Three Types Skeletal Smooth Cardiac Muscles containing this tissue usually are attached to bones and controlled by conscious effort Cells, or muscle fibers, are long and threadlike Muscle fibers contract when stimulated by nerve action and then relax immediately. In the walls of hollow internal organs Usually, it’s controlled by involuntary activity Found only in the heart Cells are joined by intercalated disks and form branched networks. Found in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves Neurons (nerve cells) Sense changes and respond with nerve impulses to other neurons or body parts Coordinate, regulate, and integrate body activities Neuroglial Cells Some forms bind and support nervous tissue Other carry on phagocytosis Still others connect neurons to blood vessels 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nerve Fiber Cytoplasm Nucleus Neuroglial cell Nuclei Cell Membrane