* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LS Chapter 18: Control and Coordination The Nervous System
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Process tracing wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
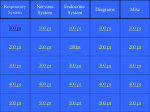
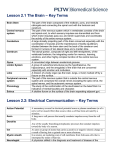
LS Chapter 18: Control and Coordination The Nervous System Group of organs that _________________, _______________ and _______________to information gathered through the senses o Acts very _______________ Can be less than 1 second between gathering and responding Touching something hot The information gathered is called a _______________ o Can be a sight, sound, taste, smell or a feeling (touch) o The reaction to the stimulus is called a _______________ If the response is involuntary, it is a _______________ Vital in the maintenance of _______________ o Keeps body’s internal conditions correct, no matter what is going on outside Split into 2 parts-The Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons _______________are the functioning unit of the nervous system o Work to relay sensory information to and from the brain 3 main parts of a neuron o _______________-Receives information o _______________-Processes information o _______________-Transmits information 3 types of neuron o _______________-Send information from senses to the brain or spinal cord o _______________-Sends information from the brain and spinal cord to tissues and organs o _______________-Connect sensory and motor neurons Information Transmission The area between neurons is called a _______________ o Neurons relay information by releasing chemicals called ______________________________ These neurotransmitters travel across the synapse from an _______________of one neuron to a _______________of another The Central Nervous System The CNS includes the ____________________________________________________________ Receives, processes, stores, and transfers information The Brain ______________________________of the body o Receives and sends information. Also processes and stores information. 3 main divisions: o _______________- Controls _______________, _______________, and _______________ ______________________________-Language center of the brain o _______________- Controls _______________muscle movement and balance Muscle memory o _______________- Controls _______________actions Heart, breathing, etc. Connects brain to the ______________________________ Lobes of the Cerebrum 4 lobes that have different functions o _______________Lobe Problem solving, emotion, reasoning, speaking, voluntary motor actions o _______________Lobe Sensation, reading, body orientation o _______________Lobe Vision, color perception o _______________Lobe Understanding language, behavior, memory, hearing The Spinal Cord Tube-like _____________________________________________that extends from the brain stem _____________________________________________to and from the brain Protected by the _______________ The Peripheral Nervous System Connects the ____________________________________________________________ 2 parts o _______________ (SoNS)- Controls _______________muscles and _______________actions o _______________ (ANS)- Controls _______________and _______________muscles (involuntary) Think: Autonomic=_______________ Damage to the Nervous System Physical injuries o _______________- Traumatic injury to the brain Can impair ability to think, concentrate, or remember Can cause headaches and blurry vision Can, in rare cases, ______________________________, and increase anxiety, anger, or loss of interest in usual activities Huge problem in sports o _______________- inability to control parts of the body, or loss of sensation Especially common in ______________________________injuries (broken neck/back) Drugs ______________________________and impair abilities o Unlike most cells, neurons do not regrow or repair Sensory System Part of the Nervous System that detects or senses the environment Humans have 5 senses o _______________ o _______________ o _______________ o _______________ o _______________ The information is collected by specialized structures called _______________ o Each sense uses different receptors Vision _______________collects and transmits to the brain Parts of the eye o _______________-outer membrane. _______________________________________it into the eye. Changes the direction to focus it o _______________and _______________- Iris is the ______________________________of the eye. Pupil is the ______________________________. The iris _____________________________________________to adjust the amount of light entering. Pupil decreases in size when bright, and _______________ (increases in size) when dark to collect more light o _______________- Changes the direction of light again to focus it on the retina o _______________-area at the back of the eye that contains cells called _______________ Photoreceptors, called _______________and _______________, send the information as electrical signals through the ______________________________to the brain Vision Problems o ______________________________- Trouble focusing objects that are far away The eye is _______________, and focuses the image in _______________of the retina o ______________________________- Trouble focusing on objects that are near The eye is _______________than normal, and focuses the object _______________the retina o _______________- Irregular curvature of cornea or lens Doesn’t bend light correctly, making image _______________ o All can be corrected with ______________________________ Hearing Done by the _______________ Sound waves are collected and transferred via ______________________________to the brain 3 parts of the ear o _______________- Collects and directs soundwaves to the eardrum (_________________________) o Middle Ear- Contains 3 tiny bones that are vibrated by the tympanic membrane Called the _______________ (hammer), _______________ (anvil), and ____________(stirrup) These bones _______________and transfer the sound to the inner ear o ______________________________- Contains the _______________, which is filled with ________ The fluid moves and disrupts _____________________, which connect to the auditory nerve The Ear and Homeostasis The ear is responsible for your ______________________________ o As you move, ______________________moves hair cells, which send information to your brain Your brain interprets them and helps you maintain balance o This is also why you may get dizzy if you have an ear infection Smell ______________________________in the nose collect sent _______________from the air Taste Chemoreceptors in the mouth (a.k.a. _______________) collect tastes and transfer them to the brain o Main tastes: _______________, _______________, _______________, _______________, and _______________ Umami is a _______________taste Especially _______________in processed foods Not all taste buds sense all tastes o There are not certain regions of the tongue for each Touch Touch receptors in the skin feel temperature, pressure, and pain o Different receptors allow for feeling _______________ _______________ (tickles) and ______________________________ (pokes or jabs) o There are more receptors in some areas than others The Endocrine System A group of _______________and _______________that release chemicals (called _______________) into the blood o _______________than the nervous system Endocrine _______________release the hormones and they travel to other areas of the body o They bond to _______________ _______________ (lock and key) Major Endocrine Glands _______________and _______________Glands in the brain o Hypothalamus _______________information from the body and signals the pituitary gland to ______________________________ o The Pituitary Gland releases hormones that ______________________________and ___________________________________________________________________________ It also releases ______________________________which allows the body to grow o The _______________Gland regulates how the body uses energy (_______________) Located in the _______________ o The _______________Gland, located in the _______________, signals the body to _______________ o _______________Glands in the abdomen release _______________to help respond to stress o The _______________secretes _______________to control blood sugar o In females, _______________release _______________and produce _______________cells o In males, _______________release _______________and produce _______________ The Endocrine System and Homeostasis The glands of the endocrine system respond to stimuli and release hormones o Helps to ______________________________ Feedback Loops o ______________________________-The glands release hormone only when needed _______________happening in the body o ______________________________- The release of a hormone ____________________________________________________________ Not as common _______________, secretion of ______________________________