* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Plasma Membrane
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
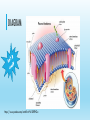
THE PLASMA MEMBRANE Period 3 honors By: Kristian Rolin Chase Denton Qwazia Lainer WHAT IS IT? The plasma membrane is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It regulates what enters and exits the cell. Cells must maintain an appropriate amount of molecules to function inside them. They must also have a way to keep things out or to allow things to enter. This is the job of the plasma membrane. The plasma membrane is like the guard at a gated community. The guard must inspect those who enter and those who leave to make sure that only the people and things needed in the community are there. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LKN5sq5dtW4 COMPONENTS OF THE PLASMA MEMBRANE Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. In the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell. Proteins embedded within the phospholipid bilayer carry out the specific functions of the plasma membrane. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mtDm2OKIK1k DIAGRAM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pfu1DE9PK2w HOMEOSTASIS The plasma membrane maintains homeostasis by keeping cell contents in and foreign material out Provides controlled avenues for the transportation of fuel, fluid and waste. "Homeostasis" means "same state." Cells in homeostasis are successfully maintaining the internal conditions necessary for basic functioning. The plasma membrane is essential for maintaining these conditions functioning. Simply, the plasma membrane separates the inside of the cell from the outside. Without it, a cell is nothing more than a popped balloon, spilling its contents out into space. HOW SUBSTANCES ENTER AND EXIT THE CELL Selectively permeable cell membranes allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by active or passive transport. Active transport processes require the cell to expend energy to move the materials, while passive transport can be done without using cellular energy. Note that the membrane can also block the passage of materials depending on the conditions inside or outside of the cell. The method used by a cell to pass molecules in or out is determined by the size of the molecule, as well as the concentration of the molecules on the inside and outside of the cell. Most cell membranes are covered with tiny protein channels that allow things to move in and out of the cell. These act as gateways. If a molecule is tiny enough to fit through a special protein channel, it will use a form of active or passive transport to move through. If the molecule is too large to fit through a protein channel, it will have to enter or exit the cell by forming a vesicle. HYPOTONIC HYPERTONIC AND ISOTONIC SOLUTIONS Plasma membranes are made up of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are chains of fatty acids attached to a phosphate group. "Bilayer" means two layers. When phospholipids get together, they form a double layer, with their phosphate groups facing out and their fatty tails pointing toward one another. The fatty interior of this layer is "hydrophobic" because it repels water. The surrounding phosphates are called "hydrophilic" because they come into contact with fluid inside and outside the cell. The plasma membrane separates these two sets of fluids and their contents. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m2xg9MzwqxA FLUID MOSAIC MODEL https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qqsf_UJcfBc https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qqsf_UJcfBc A model that describes the structure of cell membranes. In this model, a flexible layer made of lipid molecules is interspersed with large protein molecules that act as channels through which other molecules enter and leave the cell. REVIEW The primary function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. To maintain an equilibrium the plasma membrane goes through homeostasis The plasma membrane acts as a barrier that only allows certain substances to enter and exit the cell through active and passive transport ANY QUESTIONS? QUESTIONS What is the function of the plasma membrane? Why is the plasma membrane described as a “fluid mosaic” Which of the following types of molecules are the major structural components of the cell membrane? a. phospholipids and cellulose b. nucleic acids and proteins c. phospholipids and proteins d. proteins and cellulose e. glycoproteins and cholesterol WORK CITED http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/biomembrane1/solutions .html http://biology.tutorvista.com/animal-and-plant-cells/plasma-membrane.html http://study.com/academy/lesson/plasma-membrane-of-a-cell-definition-functionstructure.html http://biology.tutorvista.com/animal-and-plant-cells/plasma-membrane.html https://www.google.com/webhp?sourceid=chrome-instant&ion=1&espv=2&ie=UTF8#q=google+images