* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary landscape wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
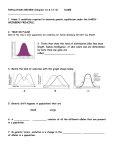
CH 22-24 Concept Questions 1. How would you respond to someone who said that evolution was “just a theory”? 2. Why do you think Darwin and Wallace formulated their ideas on natural selection at about the same time? 3. Discuss the significance of each of the following scientific advances for evolutionary theory: a. elucidation of the principles of chromosomal inheritance b. the discovery of DNA, its structure, and the universal genetic code c. technology that allows us to sequence long segments of DNA 4. How do deleterious, natural, and beneficial mutations differ? 5. Can you explain how natural selection results in an increase in the frequency of beneficial alleles in a population over time, and a decrease in the frequency of deleterious alleles? 6. How can genetic drift cause large changes in small populations? 7. How do self-fertilization and sexual selection differ in their expected effects on genotype and allele frequencies over time? 8. Explain how homologous structures and vestigial structures (the anatomical record), provide evidence for evolution. 9. Why is the concept of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium important even though the assumptions on which it is based are never completely in nature? 10. Although the stringent of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are never met completely in real populations, the genotype frequencies of many populations do not deviate significantly from Hardy-Weinberg expectations. Can you explain why? 11. Suppose you examine a population of toads breeding in a single pond and find that heterozygous genotypes at several different loci are present at significantly lower frequencies than predicted by Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. What are some possible explanations? 12. What are the different expected outcomes of stabilizing, directional and disruptive selection? Provide an example for each one. 13. Why would you expect selection of human birth weight to be stabilizing rather than directional? 14. Can you think of examples of extreme phenotypes in animal or plant populations that could be explained by directional selection? 15. How does convergent evolution and the biogeographical distribution of species reflect the outcome of evolutionary diversity?