* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tumour Analysis-Lynch Syndrome
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetic clock wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
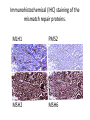
Tumour Analysis-Lynch Syndrome Dr Alan Donaldson Consultant in Clinical Genetics Bristol Why do tumour analysis? • To identify 1-5% of individuals whose colon cancer may be due to Lynch syndrome, for DNA analysis. • ~15% of colon cancers are MSI high. – Generally have a better outcome. – Poorer response to 5 Fluorouracil? Lynch Syndrome. Hereditary non polyposis colorectal cancer – HNPCC. • • Autosomal Dominant disorder. Due to mutations in one of the mismatch repair genes. – – – – – • MSH2 MLH1 MSH6 PMS2 (TACSD1) 50% 40% ~7% <5% ~1-2% Accounts for 1-5% of all colon cancers. Mismatch repair function. MSH6 MSH2 MSH3 HmutS HmutS TTT TTTT TTTTTTTT TTT TTTTT TTTTTTTTTTTTTT ? PMS1 MLH3 HmutL PMS2 MLH1 Amsterdam Criteria • Three or more family members, one of whom is a first degree relative of the other two, with HNPCC-related cancers*. • Two successive affected generations. • One or more of the HNPCC-related cancers diagnosed before age 50 years. • Exclusion of (FAP). * Colon, endometrial, small intestine, hepatobiliary, urinary tract. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of the mismatch repair proteins. MLH1 PMS2 MSH2 MSH6 Microsatellite instability (MSI) 1. Normal tissue Tumour tissue Arrows indicated additional peaks and microsatellite instability. Sporadic loss of MLH1. • 10-15% of all colorectal cancers. • Associated with DNA methylation. • Associated with BrafV600E in colonic tumours, but not endometrial. Advantages / disadvantages of MSI. Advantages. • Better sensitivity & Specificity than IHC. • Able to detect BRAFV600E mutations. • • Disadvantages. More expensive than IHC. Doesn’t tell you what gene is involved. Who is ordering these tests? Dermatology Oncology Gynaecology Surgery? Pathology? Genetics Any Questions?