* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurons
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
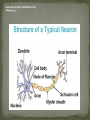
A neuron is the functioning cell unit in the nervous system that is also known as a nerve cell. Neurons are responsible for sending impulse messages to other neural cells. Impulse messages in a neuron are sent via the release of neurotransmitters. The neuron's cell body is called the soma. The neuron cell consists of 3 main sections a soma, axon, dendrite. http://scientopia.org/blogs/scicurious/2011/05/04/science-101-the-neuron/ Axon - Is the lengthy thin straight structure that is part of the neuron body (soma) that conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body to Is the tree branch like structure connected to the neuron's terminal buttons. the nerve cell body (soma) that sends and receives information between cells. Can be thought of as the brain's traffic cops routing messages to their desired cell target Dendrite - the structural space between neurons in the nervous system that is the conduit for a neuron to send a chemical message signal to the targeted neural cell. A synapse is also known as the terminal button Synapse -. Once a message is received at the postsynaptic cell an electrical message is released and passes through the adjoining neuron to the next pre-synaptic cell that releases another chemical message. The process will repeat it self until the message reaches it desired target. The word synapse is Greek in origin and means point of contact http://scientopia.org/blogs/scicurious/2011/05/04/science101-the-neuron/ Neuron Forest The real work of your brain goes on in individual cells. An adult brain contains about 100 billion nerve cells, or neurons, with branches that connect at more than 100 trillion points. Scientists call this dense, branching network a "neuron forest.“ Signals traveling through the neuron forest form the basis of memories, thoughts, and feelings http://www.alz.org/braintour/neuron_forest.asp neuronarrative.wordpress.com http://www.alz.org/braintour/signal_activity .asp The Epileptic Focus The place from where the seizure originates is called the epileptic focus. Neuron cells in this area tend to be electrically unstable. At any given time, some neuron cells are firing; others are getting ready to fire while still others are resting. During a seizure a large group of neuron cells start firing all at once. When a large group of unstable neurons start firing all at once, it causes the next group of neurons to fire, which has the same effect on the next and so on. This results in a seizure. ieaecell.org