* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Let`s Talk About Sex
Sexual objectification wikipedia , lookup
Homosexualities: A Study of Diversity Among Men and Women wikipedia , lookup
Homosexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sexual addiction wikipedia , lookup
Sexual abstinence wikipedia , lookup
Hookup culture wikipedia , lookup
Sexual racism wikipedia , lookup
History of homosexuality wikipedia , lookup
Age of consent wikipedia , lookup
Penile plethysmograph wikipedia , lookup
Sexological testing wikipedia , lookup
Body odour and sexual attraction wikipedia , lookup
Ages of consent in South America wikipedia , lookup
Sexual stimulation wikipedia , lookup
Sexual fluidity wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dysfunction wikipedia , lookup
Human mating strategies wikipedia , lookup
Erotic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Heterosexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Age disparity in sexual relationships wikipedia , lookup
Ego-dystonic sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Sex in advertising wikipedia , lookup
Human male sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sex and sexuality in speculative fiction wikipedia , lookup
Rochdale child sex abuse ring wikipedia , lookup
Sexual ethics wikipedia , lookup
Lesbian sexual practices wikipedia , lookup
History of human sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Human sexual response cycle wikipedia , lookup
Human female sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Slut-shaming wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal hormones and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
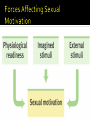
AP PSYCHOLOGY -Both nature and nurture play are role in gender Biological and socially constructed Gender Roles- set of expectations(norms) about a social position, how one acts Gender Identity- our sense of being male/female Gender Typing- popular culture determines roles Nature- sex is determined by our 23rd chromosome pair XX=Girl XY=Boy Turners Syndrome: Kleinfelters Syndrome Double Y Syndrome Fragile X Syndrome Intersexed- socially constructed term/category born with a reproductive or sexual anatomy that “doesn’t fit” into classifications of male/female “sex spectrum” Assumes that children learn by genderobserving and imitating. Being rewarded or punished… operant and classical conditioning.. Lenses through which we see the world Combination of SLT and cognition Unit 8 : Sexual Motivation Pages 348 -354 Human Sexuality refers to the ways in which people experience and express themselves as sexual beings; the awareness of themselves as males or females; the capacity they have for erotic experiences and responses. Complete Activity 3-5. Cross cultural study including 37 countries. Do females and males differ in regards to their mate selection/preference? What factors play a role in one’s mate preference? How does your preference measure up to the research findings. Characteristics Preferred by Males Characteristics Preferred by Females 1. Kindness & Understanding 1. Kindness & Understanding 2. Intelligence 2. Intelligence 3. Physical Attractiveness 3. Exciting personality 4. Exciting Personality 4. Good Health 5. Good Health 5. Adaptability 6. Adaptability 6. Physical Attractiveness 7. Creativity 7. Creativity 8. Desire for Children 8. Good Earning Capacity 9. College Graduate 9. College Graduate 10. Good Heredity 10. Desire for Children 11. Good Earning Capacity 11. Good Heredity 12. Good Housekeeper 12. Good Housekeeper 13. Religious Orientation 13. Religious Orientation Inis Beag, a small island off the Coast of Ireland – one of the most naïve and sexually repressive societies in the world. Mangaia, an island in the South Pacific have an abundance of sexual experiences in sharp contrast to Inis Beag. Mehinaku, Brazil Sexual Expression varies dramatically with time and culture. http://globalnews.ca/news/1613505/candidate-forburnaby-mayor-promises-to-ban-kissing-inpublic/ Sex is a natural desire…from an evolutionary perspective…that’s how and why we are all here!!!! What is Sex? a physiologically based motive, like hunger, but it is more affected by learning and values however, sex is NOT a need like hunger…the sex drive can be suppressed, until the urge subsides, which would be unwise in the case of hunger. Related to the concept of delayed gratification. What is the difference then between a NEED and a DRIVE? A need is a psychological feature that arouses an organism to action toward a goal, giving purpose and direction to behavior. A drive is based on the principle that organisms are born with certain psychological needs and that a negative state of tension is created when these needs are not satisfied. The Sexual Response Cycle N=382 females & 312 Males Sexual Response Cycle the four stages of sexual responding described by Masters and Johnson Excitement – genitals become engorged with blood.In women, the vagina expands and secretes lubricant and her breasts and nipples enlarge/harden. In males, the penis becomes slightly erect. Plateau – Excitement peaks. Breathing, pulse and blood pressure rates continue to increase. Orgasm feels imminent. Orgasm – Muscle contractions appear all over the body and the sympathetic nervous system is still increasing. Pleasurable feelings of sexual release occur. Resolution – Blood is slowly released from engorged areas and gradually returns to its normal state…unaroused state. Resolution Phase resting period after orgasm, during which a man cannot achieve another orgasm AP Students….remember the refractory phase of neural firing…once a neuron has fired it needs time to repolarize/recover to fire again…its all or nothing… Differences between the sexes… Estrogen a sex hormone, secreted in greater amounts by females than by males known as the female sex hormone. Women are “in heat” so to speak during ovulation. Ovulation is when the ovaries discharge an egg down the fallopian tube where it might be met by a sperm and become fertilized. Testosterone Main sex hormone in males. Hormones influence us throughout our lives… Prenatal environment = development of male vs. female. Puberty = surge in hormones ushers in adolescence. Menarche – first period. Late adult years = sexual behavior. Surgery, child birth and drugs can cause hormonal shifts. Sexual Maturation for girls is around 12 years old, for boys it is harder to collect data – usually around age 13. Across cultures, researchers have found a point at the end of male adolescence when mortality suddenly shoots up. This peak, called the "accident hump," correlates with the time of peak testosterone production in men. With high testosterone, young men are more likely to engage in risky shows of machoism and recklessness, increasing their death rate noticeably. 1. Men show greater sexual desire than women do. (men think more about sex, report more frequent fantasies and rate the strength of their sex drive higher than women do). 2.Women tend to emphasize committed relationships as a context for sexuality more than men do. Ie. Women prefer a familiar partner, affection and commitment. 3.Aggression is more closely linked to sexuality to men than to women. Ie. Shades of Grey & Gomeshi 4. Women’s sexual beliefs and behavior are more easily shaped by cultural, social and situational factors. http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/general-adaptation-syndrome-definitionphases-changes.html Unit 8B on Stress & Health (page 387) includes Hans Selye described three predictable stages the body uses to respond to stressors. The first stage is the alarm stage, which provides a burst of energy.(like the EXCITEMENT PHASE) In the second stage, known as the resistance stage, the body attempts to resist or adapt to the stressor.(like the PLATEAU PHASE) The last stage is known as the exhaustion stage because energy is depleted. (like the ORGASM & RESOLUTION PHASES) Involves physical (biological), psychological and interpersonal causes. Physical Causes – both organic factors & drugs ▪ Relationship between erectile dysfunction & diabetes. ▪ Diseases of the heart & circulatory system are particularly likely to cause erectile dysfunctions. ▪ Anxiety ▪ Alcoholics experience erectile disorder, orgasmic disorder and the loss of desire. ▪ Morphine and heroine also supress sexual desires. Psychological Causes Anxieties such as fear of failing. “Stage fright” or “performance anxiety”. Cognitive interference – “spectatoring” – the person is distracted from the erotic experience itself and steps outside the sexual act to evaluate how he or she is doing. Failure to communicate – many people do not convey their sexual desires. Prior learning – sexual abuse. Interpersonal Causes Disturbances in a couple’s relationship can produce disorders. Anger, resentment and conflict. Ie. Infidelity. Fear of intimacy. Same drives, different attitudes Births to unwed parents What’s the difference between Gender Identity & Sexual Orientation? Gender Identity is a person's private sense, and subjective experience, of their own gender. This is generally described as one's private sense of being a man or a woman, consisting primarily of the acceptance of membership into a category of people: male or female. Sexual Orientation an enduring sexual attraction toward members of either one’s own gender (homosexual orientation) or the other gender (heterosexual orientation) Lesbian – homosexual women Gay – homosexual men Bisexual – men and women who prefer sex with both females and males. Questioning – those who are questioning their sexual orientation – undecided as to where they sit on the Sexual Spectrum. Transgendered – people who have undergone sexual transformation or who believe themselves to be a different gender than the one they inhabit currently. http://www.huffingtonpost.ca/2013/06/10/ca nada-homosexuality_n_3412593.html Sexually Transmitted Infections Rates are on the rise. 2/3 of new infections are those under 25. Teenage girls are more susceptible because of their less mature biological development and lower levels of protective antibodies. Condoms offer no protection against skin to skin STIs and only partial protection against HPV (vaccination can be used as a preventative measure) HIV transmission can be reduced by condom use. Womens’ AIDs rates are increasing as transmission between male to female is higher and more likely. http://life.nationalpost.com/2013/10/22/sex-survey-reveals-nearly-a-quarter-of-canadian-universitystudents-abstain-but-many-others-avoid-condom-use/ http://www.huffingtonpost.ca/2011/11/11/sexually-transmitted-infections-university-_n_1088144.html Why does it happen? Ignorance of birth control. Guilt related to sexual activity. Minimal communication about birth control. Alcohol and drug use. TV and movies which model unsafe sex or glorify/hollywoodize teen pregnancy. Ie. Sixteen & Pregnant. #1 quality leading to sexual restraint? Engagement…those that are engaged in school (learning), their religion, their families or prosocial projects buffer themselves against early sexual experiences. Find your group Pick an article (find it in my pile or on your own) Read it and plan your presentation Presentations will take place next Wednesday! You will have time today and maybe on Monday! We will be moving on to Sensation and Perception on Monday