* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Flat Rock Community Schools
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA paternity testing wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
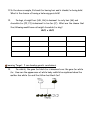
Name: __________________________________ Hour: _______ Date: ____________________ 8th Grade Genetics Test Study Guide The test will be on __________________________________ and will be 25 multiple choice questions. Learning Target: I can create a DNA model & explain how the structure of DNA causes mutations. 1. Draw 2 homologous chromosomes with heterozygous alleles. 2. Draw 2 homologous chromosomes with homozygous dominant alleles. 3. Draw a picture of DNA and explain the reasons why we study DNA. 4. Cancer can be caused by genetic factors or environmental factors. Will cancer caused by an environmental factor be passed onto offspring? Explain. 5. A male sex cell has a mutation chromosome 8. The female sex cell does not have a mutated sequence. Will the child show the mutation? 6. DNA contains the structures for making ________________ in the cell. Learning Target: I can explain how traits are passed down to each generation through chromosomes. 7. If 2 parents don’t have a trait but they have a child who does, how does this occur? 8. A female guinea pig is homozygous dominant for black fur and is mated with a male homozygous recessive for white fur color. In a litter of 8 offspring, there would probably be ______________. 9. A child is diagnosed with a lethal genetic disease. Neither parent has the disease. How might the child have inherited the disorder? Learning Target: I can use a Punnett Square to determine probability of traits being inherited. 10. What is the genotype in the highlighted quadrant in the Punnett Square below? B b B b 11. In the above example, B stands for having hair and b stands for being bald. What is the chance of having a heterozygous child? 12. In dogs, straight hair (HH, Hh) is dominant to curly hair (hh) and chocolate fur (FF, Ff) is dominant to tan fur (ff). What are the chance that the following would have a straight chocolate fur dog? HhFf x HhFf Learning Target: I can develop genetic conclusions. 13. In rabbits, the gene for black fur is dominant over the gene for white fur. How can the appearance of white baby rabbits be explained when the mother has white fur and the father has black fur? 14. A cross between a white flower and a red flower gave all pink flowers. Which is the most likely explanation for these results? 15. Kernel color in corn is a trait determined by two alleles. The dominant allele (P) produces purple color, and the recessive allele (p) produces yellow color. The diagram below shows an ear of corn produced by crossing two corn plants. The shaded kernels are purple, and the unshaded ones are yellow. What can the yellow kernels best be described as? (Be sure to look at which color has more kernels!) 16. Which of the following terms applies to traits, such as human hair color, that are controlled by more than one gene? 17. A long haired guinea pig is crossed with a short-haired guinea pig and all of the offspring are short-haired. This indicates what type of inheritance pattern? (Short hair must be this.) 18. In smiley faces, eyes can either be round (RR), star (SS), or round with a star (SR). What does this show? (Hint: Both shows – it is not a blend.) 19. Using the above example, how what is the probability of a round eyed smiley face having a child that resembles it when the partner is a round star eyed smiley face? 20. Leaves from two white clover plants, each with a different pattern, are shown below. Learning Target: I can model how DNA affects production of different proteins and explain how that is linked to mutations. 21. Students in class had to develop a model to explain how DNA codes for traits. What would be the main part of the model to show how DNA codes for traits? (How does DNA code for traits?) 22. The students using this model then had to explain what happens with mutations. How would you describe what happens with mutations using a model? Learning Target: I can explain how genetic variation affects survival. 23. The graph below shows the percentage of a large population that expresses a certain recessive trait (bb) through 10 generations. What would most likely happen if a mutation of allele b occurred after the tenth generation? 24. Looking at this graph, predict why the population showing the recessive trait has decreased. Learning Target: I can explain how genetic variation affects survival. 25. Explain how gene therapy affects cells of an individual.