* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT: Mitosis, Meiosis, DNA, PS
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
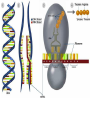
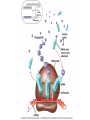
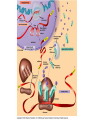
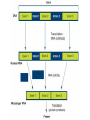
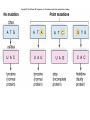
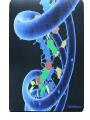
DNA / RNA DNA • Deoxyribonucleic Acid • Located in the nucleus / never leaves the nucleus • Makes up the chromosomes • 4 Nitrogenous Bases: – A = Adenine – C = Cytosine – T = Thymine – G = Guanine – A = Adenine – C = Cytosine – T = Thymine – G = Guanine • A & T – Pair up together • C & G – Pair up together • DNA is “Double Stranded” / “double helix” RNA • • • • Ribonucleic Acid Single Stranded Can move from nucleus to cytoplasm 4 Bases: – A = Adenine – C = Cytosine – U = Uracil – G = Guanine RNA – A = Adenine – C = Cytosine – U = Uracil – G = Guanine • A & U = Pair up together • C & G = Pair up together • Three main types: – mRNA = Messenger RNA • Transfers message from nucleus to cytoplasm • CODON = 3 mRNA bases code for Amino Acid – tRNA = Transfer RNA • Hooks up w/mRNA and holds the Amino Acid • ANTICODON = 3 tRNA bases match up w/mRNA and carry Amino Acid – rRNA = Ribosomal RNA • Ribosomes “workbench” for Protein Synthesis • A long chain of Amino Acids make up a ____________ – PROTEIN Protein Synthesis “Making Proteins” Transcription • Transcription: – Making RNA from DNA • mRNA Translation • Making a Protein or (polypeptide) from mRNA • Intro: Protein Synthesis: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=suNsV0cT6c • BIOFLIX: Protein Synthesis: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5wMq HOf692E Exons Vs Introns • Exons – “Expressed part of the DNA • Intron – Not expressed / spliced out – RNA splicing: Enzyme: spliceosome Frame Shift Mutation Frame Shift Example • THE FAT CAT ATE THE HAT • With the “F” deleted –THE ATC ATA TET HEH AT- • With the “F” copied twice –THE FFA TCA TAT ETH EHA T-- DNA P/S LAB • Heredity = passing of traits from one generation to the next • Variation = Parents & offspring are different • Genetics = scientific study of heredity and variation • Gametes = haploid = with only one set of chromosomes • For humans: – haploid number is 23 (n = 23) – Each set of 23 consists of 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome • In an unfertilized egg (ovum), the sex chromosome is X • In a sperm cell, the sex chromosome may be either X or Y Where do your traits come from? • Children do not inherit traits from their parents, they inherit genes. • Genes are segments of DNA • Each gene has a specific locus (location) on a certain chromosome • One set of chromosomes is inherited from each parent • Reproductive cells called gametes (sperm and eggs) unite, passing genes to the next generation Sex Chromosomes • The sex chromosomes are called X • Human females: and Y – Two X’s chromosomes (XX) • Human males: – one X and one Y chromosome • The 22 pairs of chromosomes that do not determine sex are called autosomes • Each pair of homologous chromosomes includes one chromosome from each parent • Human somatic cells: – 46 chromosomes – 2 sets of 23 (one from the mother and one from the father) – Diploid = 2n • Gametes = haploid = with only one set of chromosomes • For humans: – haploid number is 23 (n = 23) – Each set of 23 consists of 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome • In an unfertilized egg (ovum), the sex chromosome is X • In a sperm cell, the sex chromosome may be either X or Y